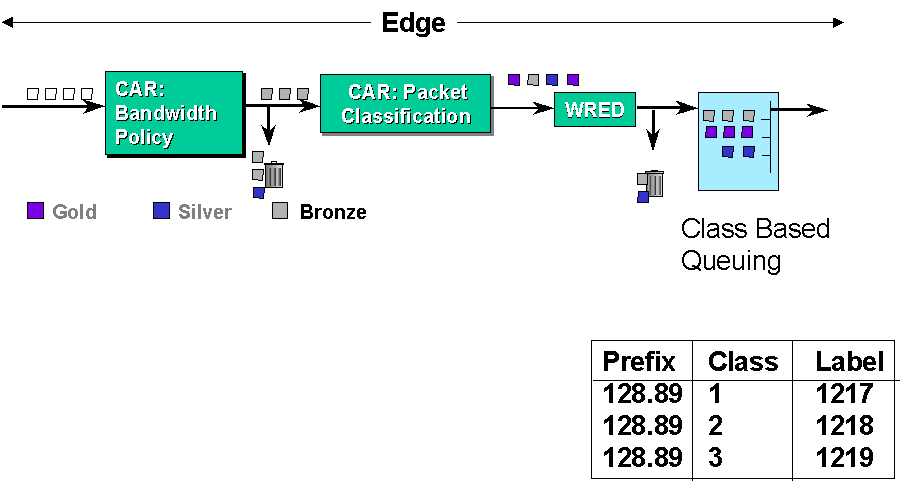
QoS
Different view of QoS
Classification of Services 應用服務之QoS分類
Demand of QoS 應用服務之品質要求
QoS Class 特性
QoS Parameters (QoS 參數)
QoS參數
QoS Parameters (QoS 參數)
Need for QoS Research
Heterogeneous Netoworks and Impedance Mismatch
QoS Problem in Multi-Access Networks
Bearer Service Architecture
QoS Architecture
RSVP and DiffServ
QoS 管理工具
Danamic Vs. Static QoS Management
MPLS QOS
MPLS QOS
MPLS QOS
MPLS QOS
| Different view of QoS |
|---|
|
User
|
Request the best quality at the lowest price
| Request the demanded quality at the lowest price
| Request the best quality at the acceptable price
| Request the torlerable quality at the lowest price
| |
|---|
|
Operator
|
Offer the best quality at the acceptable price
| Offer the acceptable quality at the highest price
| Offer the tolerable quality at the lowest price
| |
|---|
|
Researcher
|
|
provide a flexible qos management infrastructure to the operator
|
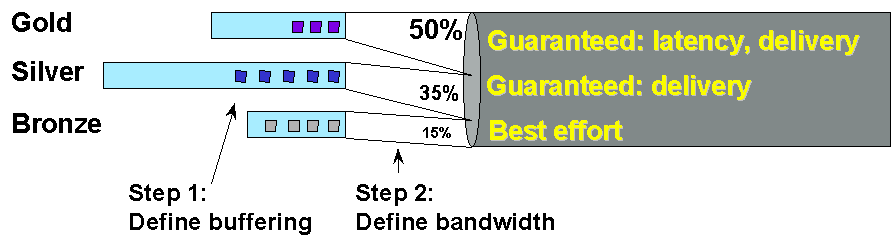
| Classification of Services 應用服務之QoS分類 |
|---|
|
Heterogeneous Service Environment
|
|
All-IP Networks must carry all types of services that
were supported by circuit and packet switching networks.
|
|
It is very diffcult to manage QoS for such environments
|
|
UMTS 組織將網路上風行的應用依時效與品質需求概略分為四大類:
|
| Classes | Examples | IEEE802.11e
| Conversational
| 語音服務 (Voice),影像電話 (Video Phone)
| 0 10ms
| Streaming
| VoD
| 1 50ms
| Interactive
| WWW, Telnet
| 2 100ms
| Background
| E-Mail
| 3 No Bound
| |
|---|
| Demand of QoS 應用服務之品質要求 |
|---|
|
QoS Components
|
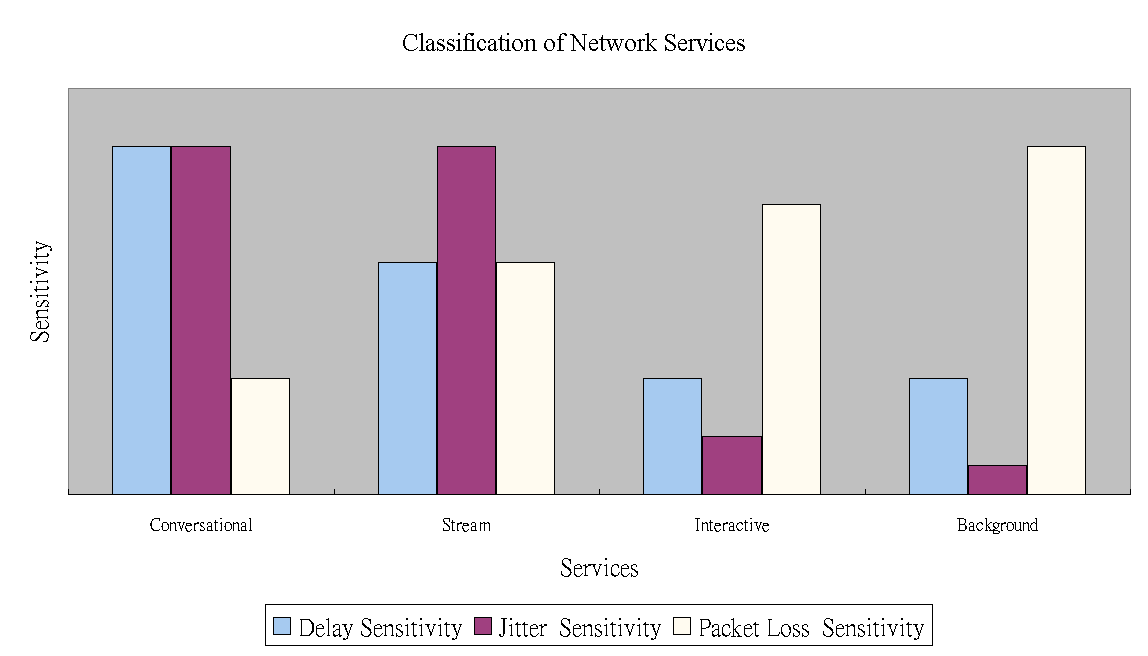
| 類別 | Delay Sensitivity | Jitter Sensitivity | Packet Lose Sensitivity | Duplex/ Simplex | Symmetry
| Conversational
| High
| High
| Low
| Duplex
| Sym
| Streaming
| Medium
| High
| Low
| Simplex
| ─
| Interactive
| Medium
| Low
| High
| Duplex
| Asym
| Background
| Low
| No
| High
| Simplex
| ─
| |
|---|
| QoS Class 特性 |
|---|
| Traffic class | Conversational conversational RT | Streaming streaming RT | Interactive Interactive best effort | Background Background best effort Fundamental characteristics
| - Preserve time relation (variation) between information entities of the stream Conversational pattern (stringent and low delay )
| - Preserve time relation (variation) between information entities of the stream
| -Request response pattern -Preserve payload content
| - Destination is not expecting the data within a certain time - Preserve payload content
| Example of the application
| voice
| streaming video
| Web browsing
| background download of emails
| |
|---|
| QoS Parameters (QoS 參數) |
|---|
⊕ Value ranges for UMTS Bearer Service Attributes
| Traffic class | Conversational | Streaming | Interactive | Background
| Maximum bitrate (kbps)
| < 2048
| < 2048
| < 2048 - overhead
| < 2048 - overhead
| Delivery order
| Yes/No
| Yes/No
| Yes/No
| Yes/No
| Maximum SDU size (octets)
| <=1500 or 1502
| <=1500 or 1502
| <=1500 or 1502
| <=1500 or 1502
| Delivery of erroneous SDUs
| Yes/No/-
| Yes/No/-
| Yes/No/-
| Yes/No/-
| Residual BER
| 5*10-2, 10-2, 5*10-3, 10-3, 10-4, 10-6
| 5*10-2, 10-2, 5*10-3, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6
| 4*10-3, 10-5, 6*10-8
| 4*10-3, 10-5, 6*10-8
| SDU error ratio
| 10-2, 7*10-3, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5
| 10-1, 10-2, 7*10-3, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5
| 10-3, 10-4, 10-6
| 10-3, 10-4, 10-6
| Transfer delay (ms)
| 100 - maximum value
| 250 - maximum value
| Guaranteed bit rate (kbps)
| < 2048
| < 2048
| Traffic handling priority
| |
| 1,2,3
| Allocation/Retention priority
| 1,2,3
| 1,2,3
| 1,2,3
| 1,2,3
| |
|---|
| QoS參數 |
|---|
⊕ UMTS bearer attributes defined for each bearer traffic class
| Traffic class | Conversational | Streaming | Interactive | Background
| Maximum bitrate
| X
| X
| X
| X
| Delivery order
| X
| X
| X
| X
| Maximum SDU size
| X
| X
| X
| X
| SDU format information
| X
| X
|
| | SDU error ratio
| X
| X
| X
| X
| Residual bit error ratio
| X
| X
| X
| X
| Delivery of erroneous SDUs
| X
| X
| X
| X
| Transfer delay
| X
| X
|
|
| Guaranteed bit rate
| X
| X
|
|
| Traffic handling priority
|
|
| X
|
| Allocation/Retention priority
| X
| X
| X
| X
| Source statistics descriptor
| X
| X
|
| | |
|---|
| QoS Parameters (QoS 參數) |
|---|
| UMTS QoS classes | VR service classes | Media type | Example VR services | Example VR application | Classification parameters
| Degree of sym.
| Delay
| Delay variation
| Information loss
| Conversational class
| Hard real-time interactive VR
| Data, graphics, audio, video, text
| Distributed simulations
| Tightly coupled flight simulation
| Two-way
| End-to-end one-way delay<100ms
| 50ms
| <3% packet loss ratio (PLR)
| Tightly coupled CVE
| Collaborative engineering and design; telesurgery
| Two-way
| End-to-end one-way delay<100ms
| N/A
| Zero
| Virtual conferencing
| Virtual char space; 3D graphics, audio communication
| Two-way
| End-to-end one-way delay<150ms
| <1ms (for conversational voice)
| 3% PLR
| Multi-user interactive games
| First person shooter game
| Two-way
| End-to-end one-way delay<100ms
| N/A
| Zero
| Soft real-time interactive VR
| Data graphics, text
| Loosely coupled CVE
| Virtual multi-user shopping center
| Two-way
| End-to-end one-way delay<400ms
| N/A
| Zero
| Multi-user interactive games
| Real-time strategy game
| Two-way
| End-to-end one-way delay<500ms
| N/A
| Zero
| Streaming class
| VR with integrated real-time streaming media (one-way)
| Data graphics, audio, video, text
| VE with integrated video/audio
| Virtual movie theater
| Primarily one-way
| Startup delay<10s Lip-synch.+-80ms
| <2s
| <2% PLR (video) <1% PLR (audio)
| Virtual humans on the Internet
| Virtual newscaster: streaming audio, video, and animation
| Primarily one-way
| Startup delay<10s Lip-synch.(animation and audio)+-80ms
| <2s
| <2% PLR (video) <1% PLR (audio) <0% PLR (animation)
| VE with integrated audio
| Ve with background music
| Primarily one-way
| Start p delay <10s
| <2s
| <1% PLR
| Interactive class
| Non-real-time interactive VR
| Data graphics, text
| Virtual place simulation on the Internet
| Virtual city tour; user navigates through multiple virtual spaces
| Primarily one-way
| One-way delay <4s/new space
| N/A
| Zero
| Database retrieval
| 3D dynamic data visualization; user interacts with data
| Primarily one-way
| One-way delay <4s/view
| N/A
| Zero
| Background class
| Non-real-time best effort VR
| Data, graphics, text
| Background download of VE
| VE requiring only initial download; all subsequent interactions/object manipulations occur locally
| Primarily one-way
| No special requirements; download time depends on size of VE Components
| N/A
| Zero
| | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
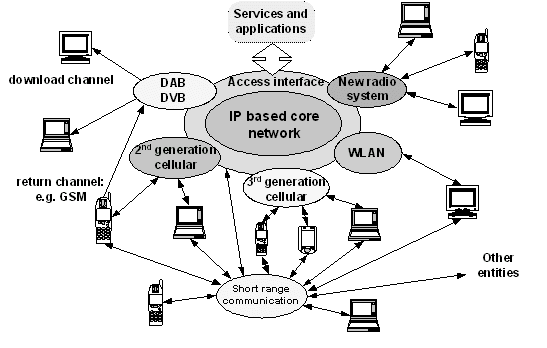
| Need for QoS Research |
|---|
|
Heterogeneous Network
|
|
下一代的網路富於異質性,且要提供多樣性的服務,
必須針對每一類服務的品質特性
提供適當的品質保證。在網路管理系統必須提供適當的資源管理機制
管理不同服務的資源運用,並讓管理者可
輕易的調校網路,使得各類服務都可以獲得適當的品質服務。
|
⊕ Routing algorithms are mostly outdated
⊕ Current QoS concerns bandwidth only
⊕ End-to-End QoS is not easy to achieve
⊕ QoS Interconnection is a big problem
⊕ Lack of proper charging mechanism
|
現有QoS研究絕大多數著重於研究既有的數據服務之 QoS,
其品質管理偏重頻寬之管理,
並不適用於欲提供全面性服務之整合性全IP網路。舉例而言,
台灣連結到美國的通訊鏈路中,有海底電纜亦有衛星通訊,
只要求頻寬的傳統數據服務並不排斥運用衛星鏈路,
但是對於 delay time 有嚴格要求的語音服務而言,
衛星鏈路即使可以提供充足的頻寬,但因傳輸距離所造成的
delay time 將嚴重影響通話品質。
|
| Heterogeneous Netoworks and Impedance Mismatch |
|---|

|
Horizontal Impedance Mismatch
|
|
網路異質性使得一個呼叫(call)/服務要求(request)可能橫跨數個特性不同的
網路,例如由一個3G手機連到3G無線接取網路,接到核心網路,
再連到一個無線區域網路(WLAN)。這些不同網路有不同的頻寬,
不同的通訊協定,不同的品質機制或參數,在網路介面上產生銜接的困難,
我們暫稱之為 impedance mismatch. 例如,一個高頻寬的 WALN 接到
一個低頻寬的 GPRS 網路時,一個呼叫 (call) 無法維持高頻寬的服務,
必須降低頻寬以配合 GPRS 的速率。又如某一段網域用DiffServ
作為品質管理機制,每一個呼叫都應該根據其品質要求被適當歸類以資提供
適當的資源,但另一個鄰接的網路卻未提供DiffServ服務,如此DiffServ
網路無足夠資訊將承接的呼叫歸類,導致 DiffServ 無法順利運作。
|
|
Vertical Impedance Mismatch
|
|
例如,DiffServ 網域的分類與下層網路(例如 ATM)不同,
兩者之間沒有一定的對應關係,難以用機械式的定義兩者之間的對應關係,
以致網路管理者必須根據實際情況將高層的
DiffServ 參數以 case by case 之方式對應到下層的 ATM (或其他種類)網路,
造成網路管理的極大障礙。因此,有必要積極投入研究,
建立系統化自動化的管理方式克服各網域之間或各種通訊協定之間的
impedance mismatch.
|
| QoS Problem in Multi-Access Networks |
|---|
|
Some multi-access networks use a contention scheme to arbitrate
access right. This contention procedure may cause some extra delay.
|
|
802.11
|
|
Cable Modem: DOCSIS
|
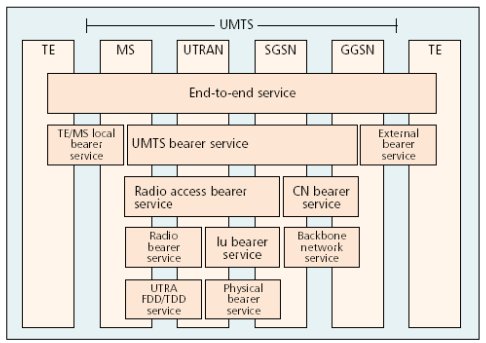
| Bearer Service Architecture |
|---|
|
User 要求 End-to-End QoS 保證
|
|
兩個端點間事實上是經過好幾個網路介接。
|
|
為滿足使用者對服務品質之要求,有必耍建立服務品質架構
|
| QoS Architecture |
|---|
|
Vertical QoS Architecture
|
| AP | Adapt to QoS Changes
| QoS Manager
| End-to-End QoS, QoS Polity, Resource Allocation
| IP
| Bandwidth+Delay+Jitter+Packet Loss, IntServ, DiffServ (EF, AF, Best Effort)
| MPLS
| Admission Control, CAR
| ATM
| piece-wise QoS, traffic engineering, CBR, rt-VBR, nrt-VBR, UBR
| Optical
| Capacity Only
| |
|---|
|
Physical Layer
|
|
在最下層的 physical 層次,對QoS 的貢獻主要在頻寬的擴增,
最常見者乃運用光纖以 DWDM 技術大幅擴增頻寬。
|
|
ATM Layer
|
|
在ATM 層則提供快速的傳輸能力,具有相當的 QoS 能力,例如
CBR, rt-VBR, nrt-VBR, UBR 等。 但是這只是針對某一個 ATM
網路的品質管制,並未能提供 end-to-end QoS,而且當初 ATM
設計時並未針對IP網路設計,故不盡符合IP網路的要求。
仍然需要透過一層 IP over ATM 的轉換,才能支援 IP網路,
不免影響效率,增加傳輸時間。
|
|
MPLS Layer
|
|
由於 ATM 之不足,而有 MPLS 之出現,試圖彌補 ATM 與 IP 之間的縫隙,
可大幅提高傳輸效率,降低 delay time, 使得 ATM 網路更適合提供即時
(real time) 的 IP 服務。但仍然無法提供 end-to-end 的 QoS。
|
|
IP Layer
|
|
在 IP 層,對於所有QoS參數 (Delay, Jitter, Packet Loss) 均需提供
相當程度的保證。目前最風行的QoS 機制是 DiffServ 與IntServ。
|
|
Above IP Layer
|
|
網路管理者必須提供 End-to-End QoS,對於資源提供適當的分配與管理,
設定 QoS Policy, 等等。 需要用到大量的作業研究技術,本計畫將著重於
本層次的 QoS 管理技術之研究。
|
|
AP Layer
|
|
在 AP 層, 必須針對不同的 QoS offer 做不同的處理。例如:
某個 user 在WLAN上看 VoD, 當他移出 WLAN 範圍,switch 到 GPRS
服務時,AP 主動降低 service grade,以保持 VoD session 持續不中斷。
又如,PoP3 信箱服務可針對用戶端的網路頻寬以決定是否
送出信件中的附檔。
|
|
分層結構
|
|
在網路尚未有統一標準之前,採用分層結構可以保有必要彈性,
可以隨著技術演進以局部方式汰換網路元件,
大幅降低開發成本與縮短開發時程。
但是分層結構不免導致效率降低,傳輸時間延遲,層間介面整合不易。
對於即時性服務而言,各層之間的轉換所造成的時間延遲與 QoS
轉換更成為絆腳石,因此,既然IP通訊協定已經成為世界共通標準,
似乎可以揚棄分層結構,直接將 IP 通訊協定建置在光纖網路上。
第一步,先將 ATM 層去掉,將 IP 協定建在 SDH 網路上,
第二步再將 IP 通訊協定建置在光纖網路上。
|
| RSVP and DiffServ |
|---|
|
IntServ 與DiffServ 之比較
|
| IntServ | DiffServ
| Granularity
| Individual flow
| Aggregate of flow
| State in router
| Per-flow
| Per-aggregate
| Traffic classification basis
| Several header fields
| DS field in IP header
| Signaling protocol
| Required (RSVP)
| Not Required
| Coordination for service differentiation
| End-to-End
| Local (per-hop)
| Scalability
| Limited by the number of flow
| Limited by the number of classes of Service
| Network management
| Similar to circuit-switched networks
| Similar to existing IP networks
| Inter-domain deployment
| Multilateral agreement
| Bilateral agreement
| |
|---|
|
RSVP based
|
|
Integrated Serivce (IntServ)
|
|
Per flow QoS
|
|
Scability Problem
|
|
DiffServ Based
|
|
Differentiated Service (DiffServ)
|
|
Per Hop QoS
|
|
Preferred
|
|
How to offer End-to-End QoS?
|
| QoS 管理工具 |
|---|
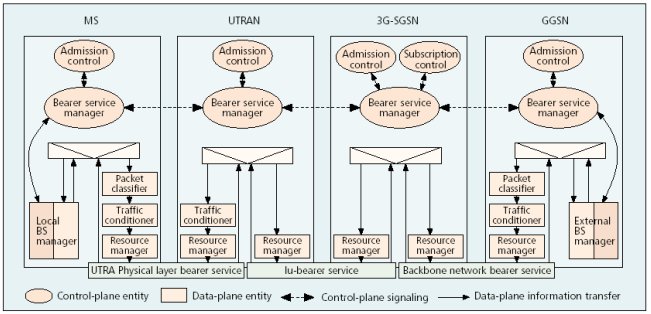
| Packet Classifier | 進行偵測並分類所接收封包的類型。
| Traffic Conditioner/Policing
| 在某些特定功能發生時,可以將分封拋棄或降低其優序的功能。
包括 Metering, Shaping, 及 Dropping 三項功能。
Metering 監控 traffice flow 流量,
Shaping 控制突發性大量封包,避免其堵塞網路,
Dropping 按優先順序捨棄封包。
| Resource Manager
| 適當分配資源的方法以滿足各個 traffic flow 的 QoS 需求,
以追求使用者整體最大利益為目標。如果可用資源不足時,
Resource Manager 應該根據排定之優先順序與最佳化原則,
進行取捨。
| Scheduler
| 當不同的 traffic flow 在一個網路元件同時競爭資源時,
這個元件應該根據排定(或動態決定)之優先順序依序處理,
以追求使用者整體最大利益為目標。
| Mapping
| 容許在網路中兩個不同組成之間的邊界上進行服務品質(QoS)的重新
Mapping. 例如,將應用服務所需之最大所能容忍之delay time,
jitter, packet loss 等等品質需求參數根據下層ATM 網路之特性,轉化成
ATM 之品質參數 (CBR, rt-VBR, 等)。
| |
|---|
|
除了個別網路元件之 QoS 管理工具之外,整體網路之管理應該還有
admission control, routing, global resource allocaion, 等工具
協助管理網路服務品質。
|
| Danamic Vs. Static QoS Management |
|---|
|
QoS 管理者最好能針對網路的品質狀態及可用的資源隨時調節
QoS policy 及相關的管理措施。但是,QoS 管理者必須能隨時
獲知網路的品質狀態,並能精確預測網路的品質,才有能力
適時調整管理措施。網路越大,此項工作越不容易做好,
所以 QoS 管理者必須對 Static 與 Dynamic QoS Management 做個取捨,
一般而言,上層的管理者需要用到較多的static management,
下層管理者因管理範圍較小,也較容易預測,可以採用較為dynamic
的管理方式。
|
| MPLS QOS |
|---|
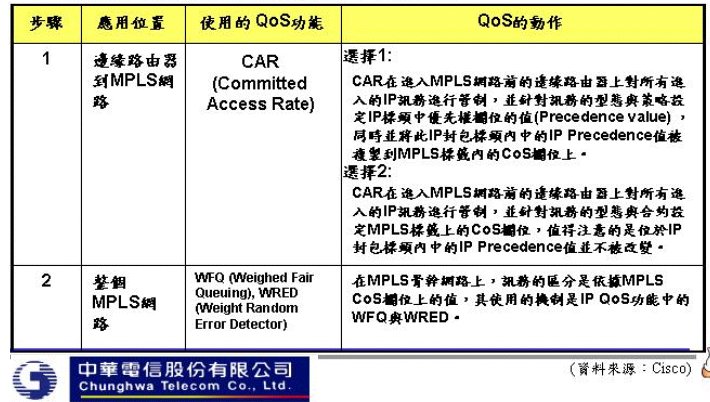
| MPLS QOS |
|---|
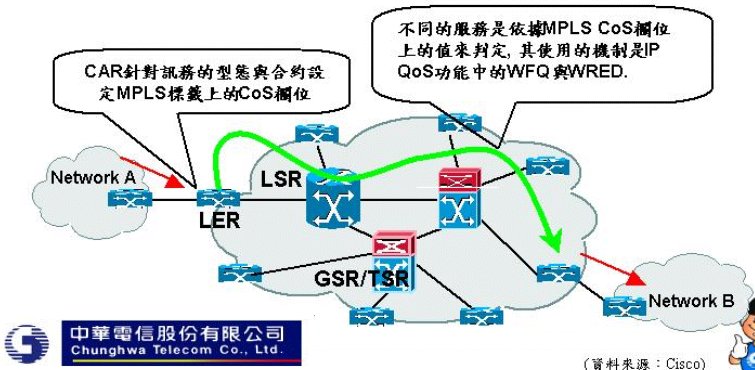
| MPLS QOS |
|---|
| MPLS QOS |
|---|