| Outline |
|---|
♦ Introduction
♦ Related Work
♦ Our Approach
♦ Performance Evaluation
♦ Conclusion
| TCP |
|---|
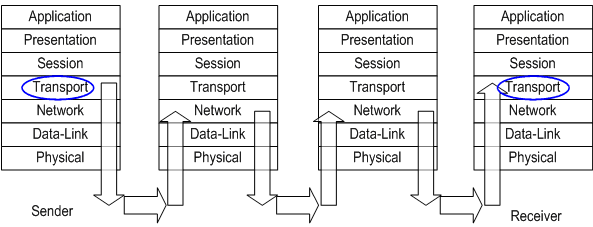
網路上被廣為使用的端對端傳輸層協定
| Reliable, in-order
| Connection-oriented
| Flow controlled
| |
|---|
| TCP |
|---|
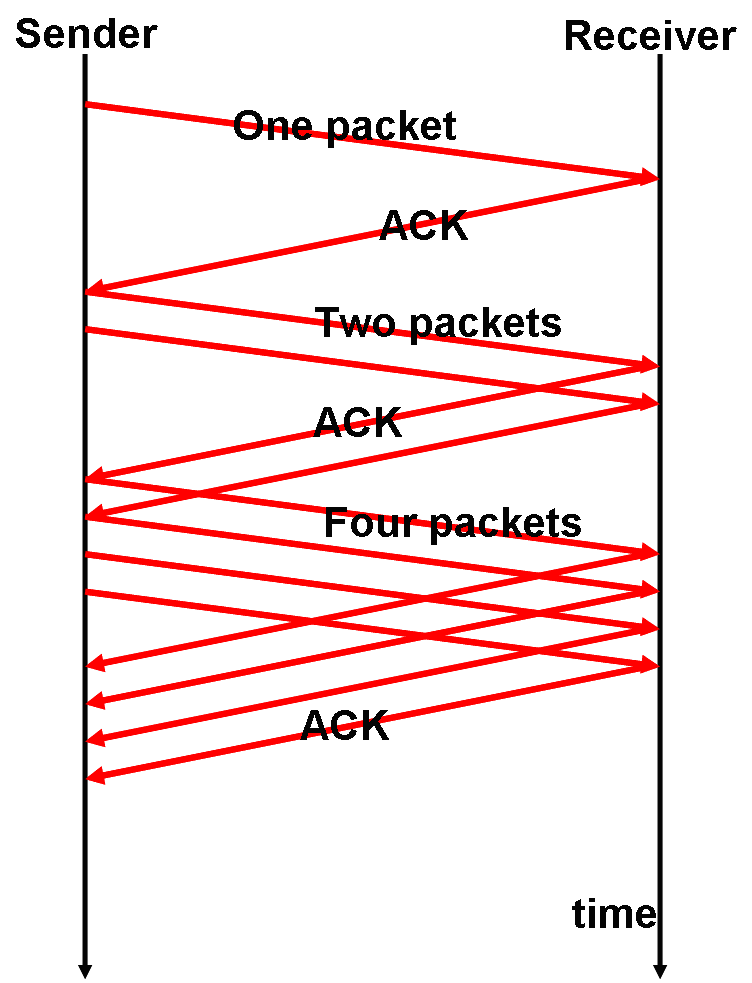
⊕ Flow control & Congestion control
♦ Trial-and-error based flow control for controlling congestion
♦ Sliding window mechanism
調整 window size = 調整 data rate

| 慢啟動 (Slow Start) |
|---|
| TCP 的設計目標 |
|---|
♦ 確保網路從sender端可以可靠的傳輸至receiver端,保證packet到達,
♦ 在不把網路塞爆的情況下盡量利用剩餘頻寬
| TCP實作相關的RFC文件 |
|---|
| RFC number | Topic
| 793
| Transmission Control Protocol
| 1323
| TCP Extensions for High Performance
| 2018
| TCP Selective Acknowledgement Options
| 2581
| TCP Congestion Control
| 2914
| Congestion Control Principles
| 3168
| The Addition of Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) to IP
| 3390
| Increasing TCP's Initial Window
| 3782
| The NewReno Modification to TCP's Fast Recovery Algorithm
| |
|---|
| TCP on MANET |
|---|
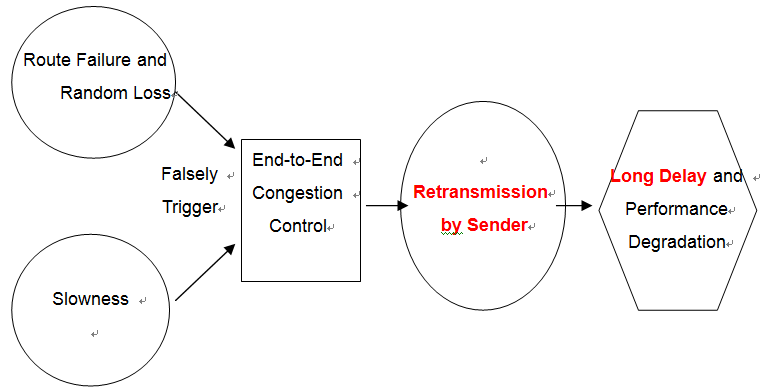
⊕ Conventional TCP may perform poorly on wiereless network
♦ Slowness and too many retransmissions
♦ Mistriggering Slow Starts for congestion control
傳統TCP的假設 packet loss 的最主要原因是因為網路壅塞
將packet loss當成congestion的indicator
將所有的loss都當成congestion loss來處理
♦ Packet loss on Wireless network may have different causes
There are many proposals to solve the problems
but few deal with reduction of retransmission
| The Causes of Packet loss on MANET |
|---|
| Slowness問題 |
|---|
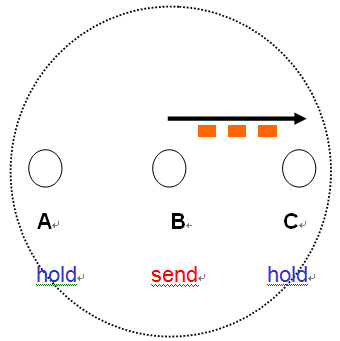
♦ On MANET (Mobile Ad Hoc Networks)
Neighboring nodes have to compete for radio channels
Inherently against packet forwarding mechanism
| Packet Retransmission |
|---|
♦ Poor radio channel may lead to too many packet losses.
♦ Retransmission from the sender may increase the chance of packet loss as well as channel competition
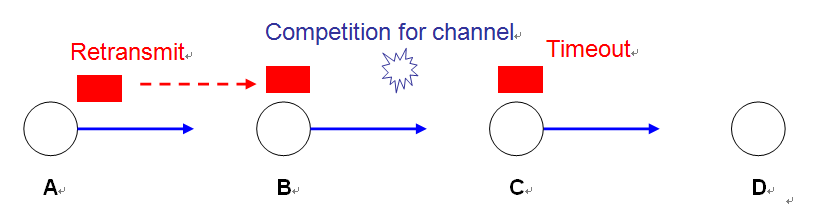
| Local Packet Retransmission |
|---|
種種原因使得常常必須重送多次才可到達目的地, 導致要耗費極長的時間才能將封包送達目的地
在行動隨意式網路中,大量傳輸資料的需求並不大, 反而是封包的快速送達更為重要,因 此加速封包的送達成為比增大傳送量更為重要的目標。
為了使封包較快送達目的地端,我們提出了Hop-by-Hop TCP 的方法,使每個節點使用當地重傳以保證封包成功的傳到下一 個節點,遺失的封包不必重新由傳送端重傳,能更快反應封包遺失, 並且提昇傳輸可靠度,使封包在高遺失率的情形之下能順利且較為 快速的送達目的地端。
| 從Sender重傳 | 從Local重傳
|
| 
|  |
|---|
| Split TCP |
|---|
| Hop-by-Hop TCP |
|---|
傳統的TCP只會在兩個端點上執行 一般而言網路的中間節點都是Router, 因此不可能會有TCP在第四層中。
在MANET中每個node可能都是computer,因此我們可以Run protocol在各個node上 我們利用MANET的這個特性,設計Hop-by-Hop TCP,使封包一站一站確保傳送,期望縮短傳送的delay time、提升throughput。
| Related Work |
|---|
♦ 利用網路提供的一些資訊分辨封包遺失原因以免不必要降速
ATCP (Ad Hoc TCP)
TCP Muzha
♦ 運用中間節點幫助傳送封包
The transport layer revisited
| ATCP |
|---|
♦ A layer called ATCP is inserted between the TCP and IP layers of the source node
♦ ATCP listens to the network state by
ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification) message
Congestion!!
ICMP “Destination Unreachable” message
Network Partitioning!!
♦ Sender can be put into 3 states:
| Persist State | by ICMP message
| Congestion Control State
| by ECN message
| Retransmit State
| by packet loss without ECN flag
| |
|---|
Note - After receiving three duplicate ACKs, sender does not invoke congestion control and puts TCP in Persist State and quickly retransmit the loss packet from buffer ( Multipath routing or channel loss)
Recomputation of congestion window size after route re-establishment
| TCP Muzha |
|---|
♦ 藉由路由器協助,提供網路內部資訊給傳送端
在未發生擁塞前不需依賴封包遺失便可進行適度的傳輸速度控制
♦ 尋找傳送路徑中的瓶頸,進而計算出瓶頸提供的可用頻寬,藉由瓶頸所提供的資訊動態的進行流量控制以充份利用頻寬並避免產生擁塞
♦ 可辨別出封包遺失的原因是否為網路擁塞所引起或是Random loss而遺失並進而作相對應的處理
| Adaptive CWL (Congestion Window Limit) |
|---|
If the congestion window size is greater than an upper bound, the TCP performance will degrade.
Find the BDP (Bandwidth Delay Product) of a path in MANET
They use this upper bound of BDP to dynamically adjust TCP’s max. window size
| The Transport Layer Revisited |
|---|
Heimlicher, Simon Baumann, Rainer May, Martin Plattner, Bernhard, “ The Transport Layer Revisited,” Communication Systems Software and Middleware, 2007. COMSWARE 2007.
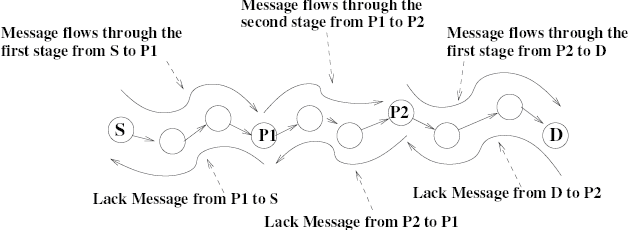
♦ The framework is implemented on two sublayers
The hop-by-hop layer runs on every node and provides per-link flow control and congestion control
On this layer, data is managed in units of fragments(8 packets)
The end-to-end layer operates at the end points of the connection, provides a reliable-byte-stream interface to the application-layer, just like TCP
Data is managed as segments, which are data units comprising a few fragments(4 fragments)
♦ The end-to-end congestion control mechanism has a job similar to the congestion control algorithm of TCP: it limits the number of un-acknowledged segments on a per-connection basis.
♦ If no acknowledgement is received for a segment for a certain period, the source needs to retransmit the segment.
♦ If a packet is lost on any intermediate link, the node at the receiving side will not acknowledge the corresponding fragment and the last hop will retransmit the fragment.
| Comments to Other Work |
|---|
♦ 如果sender沒收到segment的ACK,則必須重傳整個segment ACK遺失則重傳overhead相當大 Segment的重傳使用exponential back-off,delay time將會拉更長
♦ 若中間節點遺失一個封包,則必須重傳整個fragment 網路環境不穩定,容易因為一個封包遺失而重新傳送沒遺失的封包
♦ 如果網路上不止有一條flow,節點一次傳送整個fragment時,其他flow的封包就必須等待較多時間,且傳送失敗的機會亦相對高。
| Summary |
|---|
♦ 目前在無線隨意式網路中大部分的方法,大都著重在於利用分辨封包遺失的原因,以減少TCP容易不必要降低傳送速率的機率,較少利用中間節點以幫助確保傳送的方法
♦ 然而在無線隨意式網路環境下,不穩定的環境使封包容易遺失
從傳送端重傳
每次從傳送端重傳會遭遇到相同的條件
造成惡性循環,不斷從傳送端重送,封包送達速度緩慢,效能低落。
| Our Approach |
|---|
⊕ Hop-by-Hop TCP
♦ 我們建議讓網路中的每個intermediate node可以一站一站進行retransmission,提昇傳輸可靠度
♦ 每個node都幫忙keep住封包
♦ 封包遺失時,只需從Local端重新發送,而不需回到sender端重送
| Hop-by-Hop TCP |
|---|
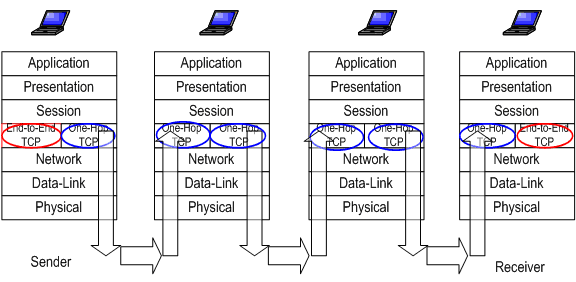
♦ 2 Components
| End-to-End TCP | running on sender and receiver
| One-hop TCP
| running on each intermediate nodes
| |
|---|

| Design Objectives |
|---|
♦ 降低平均delay time使封包能快速送達
♦ 減少Number of retransmission
♦ 提升throughput
♦ 和其它協定共存時(NewReno),仍能保有相當的效能
| Design Issues |
|---|
♦ 速度調控 : 如何不造成congestion並有效利用頻寬
♦ 如何維持 Fairness
♦ 如何處理 End-to-End packet loss
♦ 如何處理 ACK loss
♦ 如何設計重傳機制
♦ 如何設計Buffer控制
♦ 如何減少重送次數
| End-to-End TCP |
|---|
♦ 用於網路的兩個端點,確保封包能從sender端成功傳輸至receiver端的protocol
♦ 延續TCP Reno的機制,但
將Sender的congestion window設定一個upper bound,使其不會過度的成長
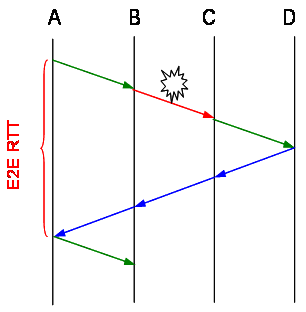
採取較大的 End-to-End RTO 避免因 slowness 而導致不必要的重傳與 Slow Start
| One-Hop TCP |
|---|
♦ 用於相鄰兩個節點之間,提升packet傳輸可靠度,保證送達下一站的傳輸層協定
♦ 功能:
Buffer packet
進行遺失封包的 Local 重傳
| One-Hop TCP |
|---|
⊕ 速度調控:
♦ 一次送一個packet過去,等待ACK回來,再送下個packet
No need for sliding window
⊕ 重傳:
♦ One-Hop RTO之內downstream node未回覆ACK則重傳封包
提昇傳輸可靠度
♦ 超過Retransmission Threshold則不再重傳
Route Failure
Congestion
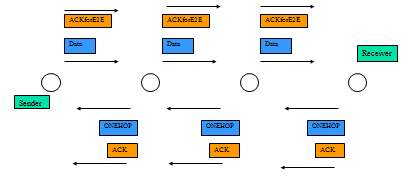
| End-to-End ACK |
|---|
| End-to-End ACK: | 傳統TCP中Receiver傳送至Sender的ACK
| 提昇End-to-End ACK 存活率之機制:
| Receiver端使用One-Hop TCP機制,將End-to-End
ACK一站一站確保傳輸成功,傳送至Sender端
|
|  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
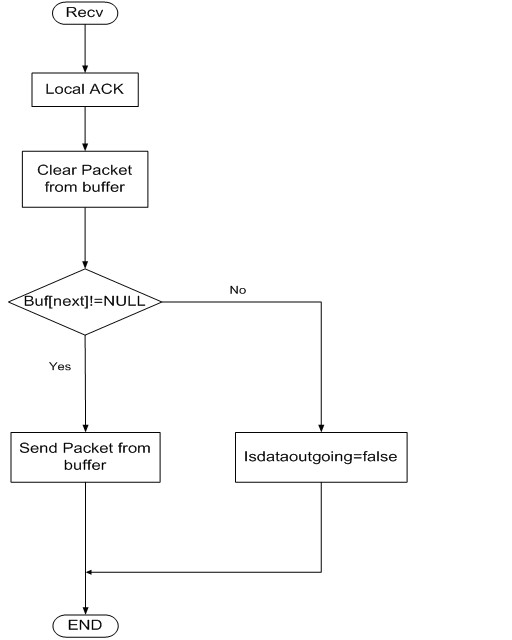
| One-Hop TCP接收Local ACK流程 |
|---|
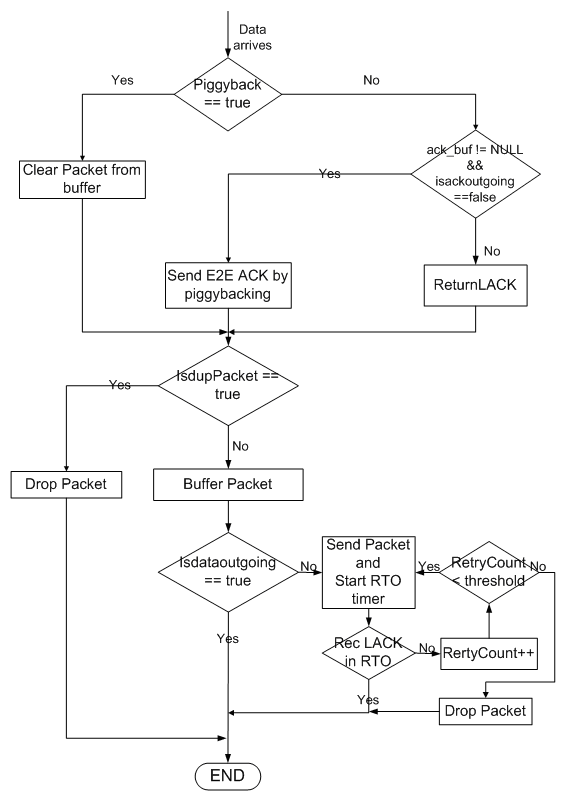
| One-Hop TCP接收資料封包流程 |
|---|
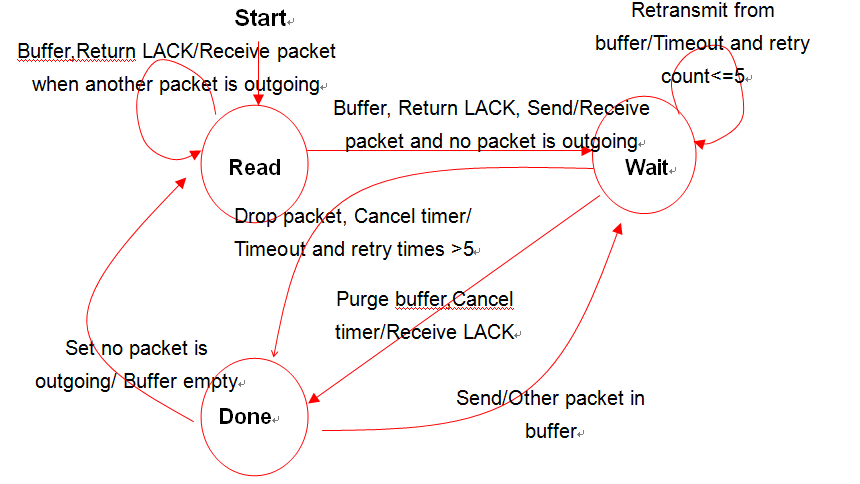
| One-Hop TCP狀態轉移 |
|---|
| One-Hop TCP機制 |
|---|
| Event | Status | Actions taken in the receiving node | Next state
| Receive a packet when flag
no_packet_outgoing is false
| Ready
| 檢查是否重複封包,若不是則暫存此封包;
回覆此封包之Local ACK,若反方向有封包欲傳送,
則piggyback上去
| Buffer the new packet; if there is any packet to be sent in another direction, piggyback it, if not, return LACK Ready
| Receive a packet and no packet is outgoing
| Ready
| 檢查是否重複封包,若不是則暫存此封包;
回覆此封包之Local ACK,若反方向有封包欲傳送,
則piggyback上去;送出封包、啟動計時器
| Buffer the new packet; if there is any packet to be sent in another direction, piggyback it, if not, return LACK, send the packet, and start timer Wait
| Local Timeout and retry count < 6
| Wait
| 重傳逾時的封包;重新啟動計時器
| Retransmit the Timeout packet; restart timer Wait
| Local Timeout and retry count > 5
| Wait
| 從暫存器清除重傳超過五次的封包;停止計時器
| Purge the packet that retransmits over five times from buffer; stop timer Done
| Receive a LACK from downstream node
| Wait
| 清除暫存器內相對應封包;停止計時器
| Purge the packet from buffer; stop timer Done
| Other Packet in Buffer
| Done
| 送出暫存器內的下一個封包,並啟動計時器
| Send the next packet from buffer; start timer Wait
| Buffer empty
| Done
| 設定為無封包正在傳送,等待接收下一個封包
| Set flag no_packet_outgoing to true; wait the next packet Ready
| |
|---|
| One-Hop TCP演算法虛擬碼(Pseudo code) |
|---|
Receive ( Packet ){
if ( Data )
{
ReturtLACK ( ) ;
if ( NewPacket_ == True )
{ BufferPacket ( ) ; }
if ( isdataoutgoing_ == False )
{
SendPacket ( ) ;
Isdataoutgoing == True;
}
}
if ( LACK )
{
PurgeBuffer ( ) ;
if ( Buffer == NULL )
{ set isdataoutgoing == False ; }
else
{ SendPacketInBuffer ( ) ; }
}
}
|
|---|
| Overhead Reduction |
|---|
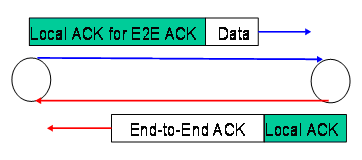
為了要減少過多 local ACK 的overhead, 我們將Local ACK for E2E ACK封包及Loacl ACK封包分 別利用Piggybacking的方式搭在Data封包及End-to-End ACK 封包上。
| Forward dats stream | | Backward dats stream
| |
|  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
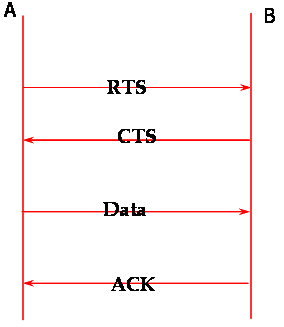
| 802.11 MAC Layer 4-Way Handshake |
|---|
| Performance Evaluation |
|---|
♦ 用NS-2模擬器評估 Hop-by-Hop TCP
⊕ 評估指標:
♦ Average Delay Time
♦ Average Throughput
♦ Retransmission
♦ CWND (congestion window size) 的變化狀況
♦ Fairness Index
| 實驗設計 |
|---|
⊕ Performance Test
| 控制變數 | hop count | error rate | buffer size |
|---|
⊕ Fairness Test
♦ 觀察多協定共存狀態下的公平性 (Fairness)
HbH 和 Reno共存的情形
| 觀察有多個Hop-by-Hop TCP flow並存時的情形
| |
|---|
| 實驗一 拓樸及參數 |
|---|
| Parameter | Range
| Buffer Size
| 50 packets
| CWND Upper Bound
| 4
| Link Bandwidth
| 0.5~1 Mbps
| Error Rate
| 0.0~0.2
| Number of Nodes
| 5~11
| MAC Protocol
| 802.11
| Routing Algorithm
| DSR
| |
|---|
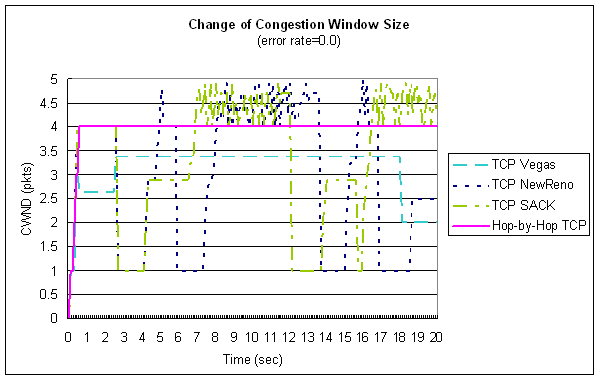
| Change of Congestion Window Size |
|---|
♦ (error rate = 0.0)
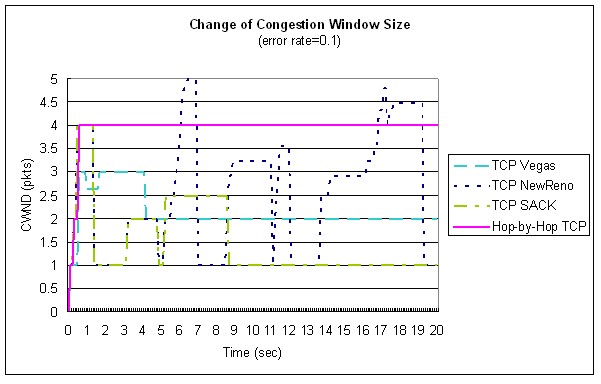
| Change of Congestion Window Size |
|---|
♦ (error rate = 0.1)
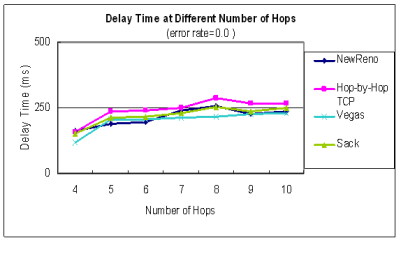
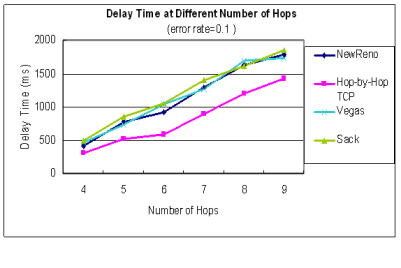
| time at different number of hops |
|---|
| error rate = 0.0 | error rate = 0.1
|
|  |  error rate = 0.2
| | | 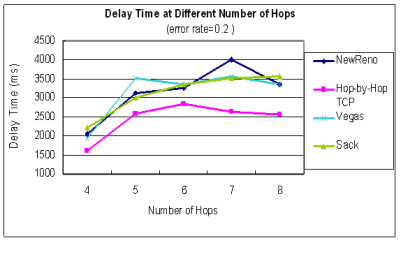
在封包容易遺失的MANET中,
遺失的封包直接從local端快速重傳而不必由sender端重傳
能縮短20%以上的Delay time
| |
|---|
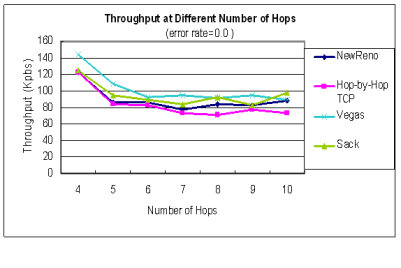
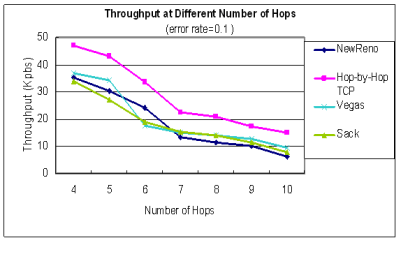
| Throughput at different number of hops |
|---|
| error rate = 0.0 | error rate = 0.1
|
|  |  error rate = 0.2
| | | 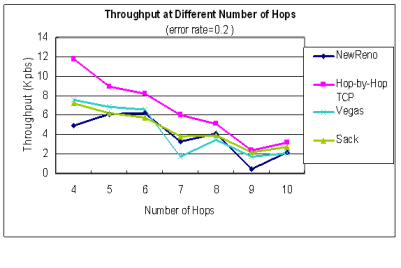
在封包容易遺失的MANET中,中間節點一站一站
確保傳送成功,使得封包到達的機率提升,
能提升25%以上的throughput
| |
|---|
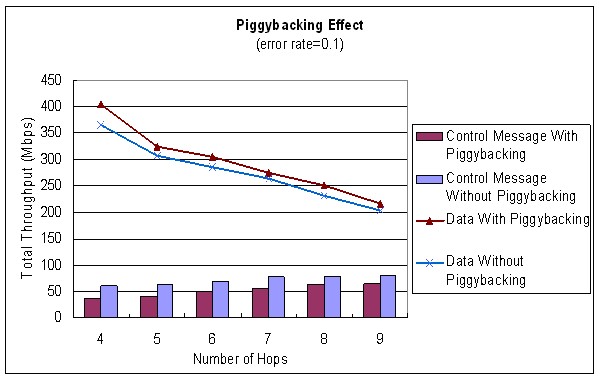
| Effect of Piggybacking |
|---|
♦ 使用piggybacking機制及不使用piggybacking機制的throughput比較
| 在傳送端重傳比率之比較 |
|---|
| error rate = 0.0 | error rate = 0.1
|
| 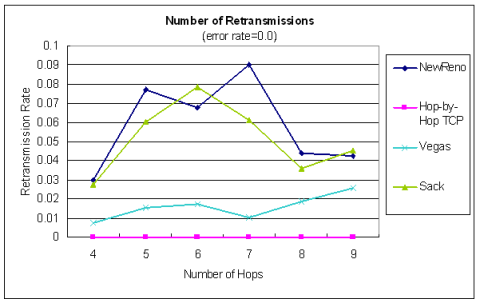 | 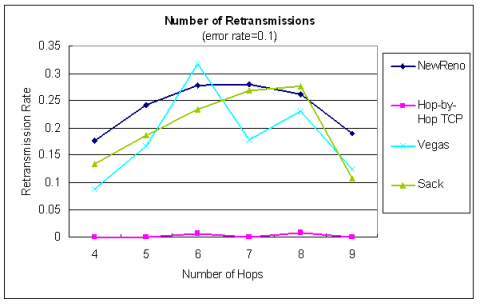 |
|---|
| Summary of Experiment 1 |
|---|
♦ 在不穩定的網路環境中,遺失的封包能從local端立刻重傳, 平均延遲時間比NewReno縮短了20%以上,整體效能高於25%以上
♦ 不會因為MANET不穩定的環境遺失封包而影響congestion window size,造成傳輸速度不 必要的降低
| 實驗2 Fairness Test |
|---|
在網路上不同版本的TCP同時使用時,會有公平性的問題 採用不同版本的 TCP flow 可能得到不同比例的頻寬
TCP Vegas 的一個問題便是它和TCP Reno共存時會因為Reno採用較具侵略性的擁塞控制方 法,因此在共存時, Vegas效能差了很多
♦ 實驗二在測試 Hop-by-Hop TCP 的公平性
| Test 2A | 測試不同 TCP 版本共存時之公平性
| Test 2B
| 測試不同時間啟動使用同一TCP 之flow 的公平性
| |
|---|
| and Parameter for Fairness Test |
|---|
| Topology | Parameter | Range
|
| 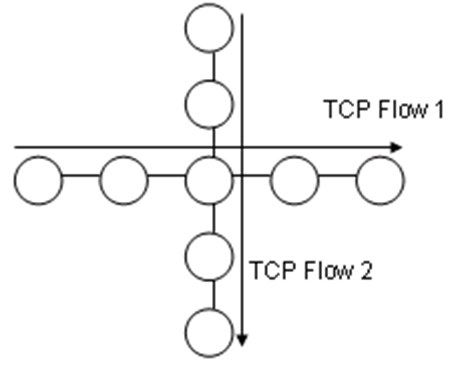 Buffer Size
| 50
| Error Rate
| 0.1
| Link Bandwidth
| 1 Mbps
| Number of hops
| 4, 6, 8
| MAC Protocol
| 802.11
| Routing Algorithms
| DSR
| |
|---|
| Jain's Fairness Index |
|---|
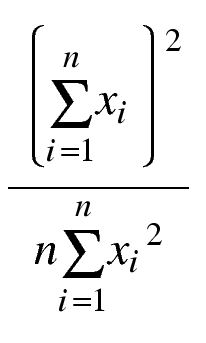
x i is the flow throughput of flow i
| equal partitioning of bandwidth achieves index of 1
| If only k of n flows receive equation bandwidth
(and others get non) index is k/n
| |
|---|
| Fairness Test 2A |
|---|
| NewReno vs. Vegas (Throughput) | NewReno vs. Hop-by-Hop TCP (Throughput)
| | 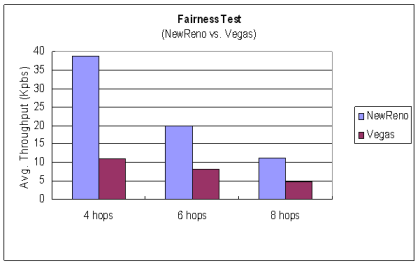 | 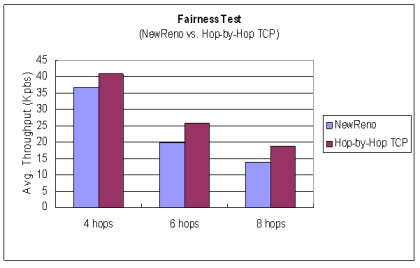 Jain's Fairness Index
| |
| 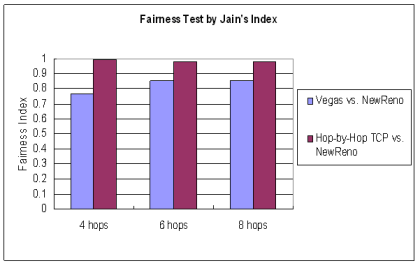 | |
|---|
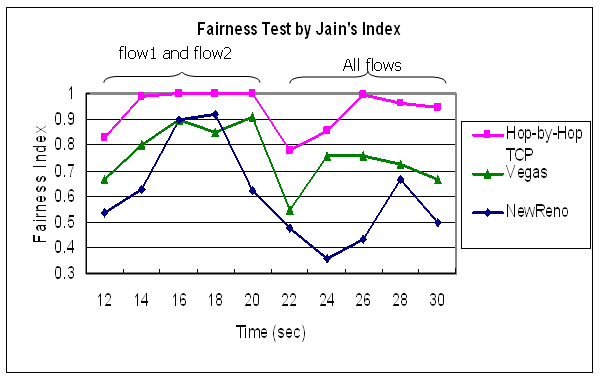
| Fairness Test 2B |
|---|
| Protocol | Throughout Dynamics | Jain's Index Dynamics
| HbH | TCP | 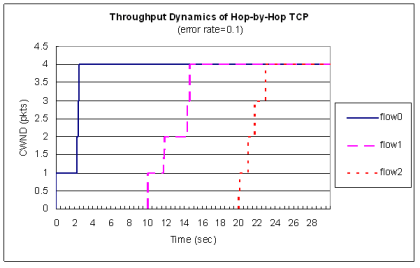 | 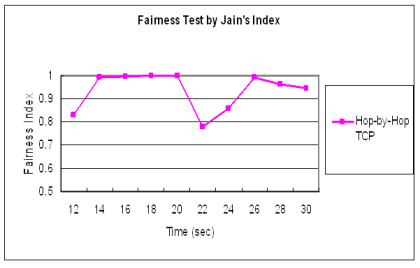 TCP | Vegas | 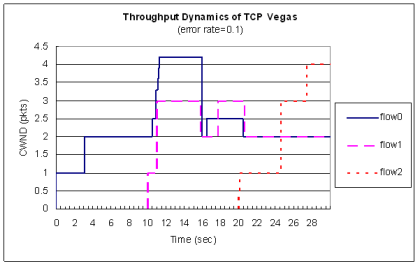 |  TCP | NewReno | 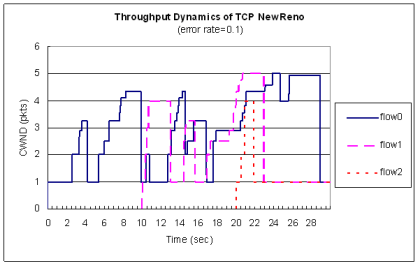 | 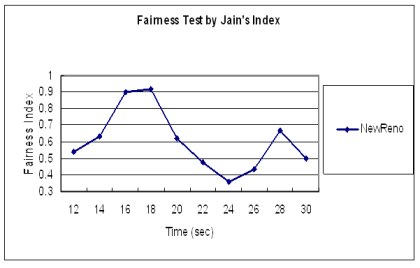 |
|---|
| Fairness Test 2B |
|---|
♦ Hop-by-Hop TCP vs. Vegas vs. NewReno
| Summary of Fairness Test |
|---|
♦ Hop-by-Hop TCP 承襲了 Reno 的擁塞控制機制 雖然效能略有下降,不至於因為Reno較侵略性 擁塞控制方法而使得效能降低過多
因此相對於Vegas較能與 Reno 等協定共存而不致於 受到排擠
♦ 在多條flow時候能達到同步化,可用頻寬較一致
每條flow在每個節點皆一次傳送一個封包 晚到的flow也能一起競爭頻道傳送,因此公平性較佳
| Conclusion |
|---|