無線電技術
A Brief History
RF Signal Propagation
RF Signal Propagation
Propagation Mechanism
頻率與波長
Decibels (dB) and dBm
Gain and Attenuation
Noise, Interference, SNR
最大頻寬 - Shannon理論
Channel Capacity
天線
電波傳播
Radio Frequency (RF) Spectrum
Spectrum Allocation
ITU-R defined ISM Bands
Spectrum Allocation - US
Spectrum Allocation - Singapo
最大頻寬限制
Multipath Interference Problem
Fluctuations of SNR
Multipath Interference Problem
其他干擾
Rain Attenuation
Doppler Effect
FSK
MultiAccess Technology
FDMA
TDMA
TDMA Time Frame
Spread Spectrum
CDMA
雙工 (Full-Duplex)
特性分析
Mobile System
| A Brief History |
|---|
| 1834 | wired telegraph for manually digitalized data (Gauss & Weber)
| 1839
| first demonstration of telegraph between Washington DC and Baltimore (Morse)
| 1858
| first transoceanic cable for telegraph
| 1867
| manually switched telephone for analog voice (Bell)
| 1897
| wireless telegram (Marconi) SMS service!
| 1900
| transoceanic wireless telegraph (Marconi)
| 1905
| Radio transmission (Fessenden)
| 1908
| idea of TV (Campbell-Swinton)
| 1915
| transcontinental telephone (Bell)
| 1920
| commercial radio broadcast (KDKA), and sampling in comm (Carson)
| 1926
| TV demonstration (Baird, England, and Jenkins)
| 1933
| FM modulation invented (Armstrong)
| 1941
| TV broadcast starts in the US
| 1946
| First computer in U. Pennsylvania
| 1950
| TDM, microwave radio, and voice band modems used in PSTN
| 1953
| Color TV and transoceanic telephone
| 1957
| first satellite (Sputnik I)
| 1962
| Transoceanic satellite TV (Telstar I)
| 1965
| videotape (Sony)
| 1968
| cable TV development
| 1968
| ARPANET started (first node at UCLA)
| 1971
| 9600 bps voice band modems (Codex)
| 1972
| Demonstration of cellular systems (Motorola)
| 1973
| Ethernet invented (Metcalfe), also international ARPANET
| 1980
| fiber optic systems applied to PSTN
| 1995
| Netscape, Internet as the first popular data communication networks
| |
|---|
| RF Signal Propagation |
|---|
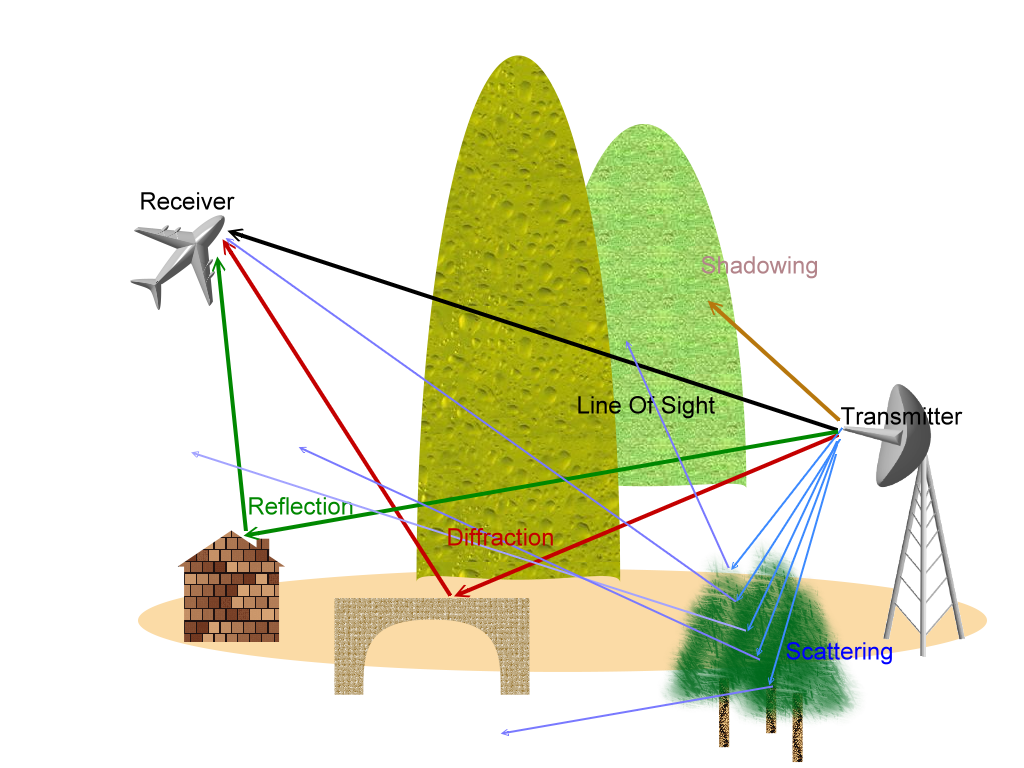
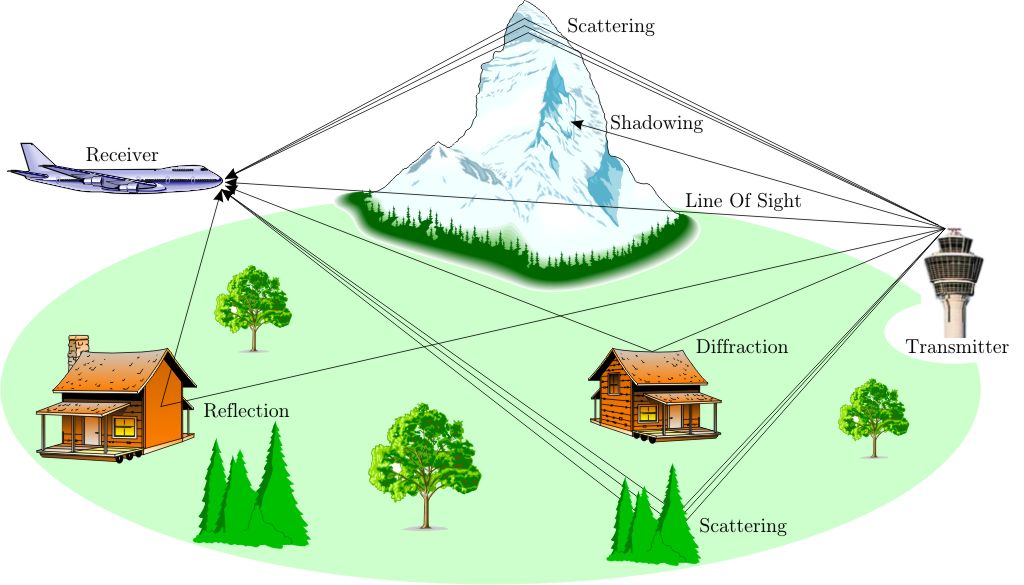
| RF Signal Propagation |
|---|
|
What is LOS problem?
|
|
Case of Signal Differection
|
|
Case of Lake effect for Cellular System
|
|
Case of Wireless Link for a Conference
|
|
Cases of RF signal hopping
|
|
Ohio Case
|
|
Circult Board Layout
|
| Propagation Mechanism |
|---|
|
Reflection and transmission
|
|
Reflection occurs when a propagating electromagnetic wave
impinges upon an
object which has very large dimensions when compared to the
wavelength of the
propagating wave.
|
|
Diffraction
|
|
Diffraction occurs when the radio path between the transmitter
and receiver
is obstructed by a surface that has sharp irregularities
(edges).
|
|
Scattering
|
|
Scatters occurs when the medium through which the wave travels
consists of
objects with dimensions that are small compared to the
wavelength, and where
the number of obstacles per unit volume is large.
|
| 頻率與波長 |
|---|
|
c = λf
|
| c | speed of light, a constant
| λ
| wavelength
| f
| frequency
| |
|---|
|
AM radio with frequency 1710 kHz equal to wavelength 175m
|
| Decibels (dB) and dBm |
|---|
| Gain and Attenuation |
|---|
| Noise, Interference, SNR |
|---|
| 最大頻寬 - Shannon理論 |
|---|
| Channel Capacity |
|---|
| Data rate | rate at which data can be communicated (bps)
| Bandwidth
| the bandwidth of the transmitted signal as
constrained by the transmitter and the nature of the
transmission medium (Hertz)
| Noise
| average level of noise over the communications path
| Error rate
| rate at which errors occur
| Error transmit 1 and receive 0 transmit 0 and receive 1 |
|---|
| 天線 |
|---|


| 電波傳播 |
|---|
 |  |
|---|---|
 | |
| Radio Frequency (RF) Spectrum |
|---|
| 頻率範圍 | 波長範圍 | 傳播特性 | 代表性用途
| 特低頻 | (VLF) 3-30 KHz
| 100,000~10,000公尺
|
1. 電波沿地球表面行進,可達長距離通信
| 2. 終年衰減小,可靠性高 3. 利用電離層與地表面形成的導層傳至遠距離 4. 地波與天波並存 5. 使用垂直天線
1. 極長距離點與點間之通信
| 2. 航海及助航 3. 感應式室內呼叫系統 低頻 | (LF) 30-300KHz
| 10,000~1,000公尺
| 同上
|
1. 長距離點與點之通信
| 2. 航海及助航 3. 感應式室內呼叫系統 中頻 | (MF) 300~3000 KHz
| 1000~100公尺
|
1. 電波於日間沿地球表面行進,達較短距離
| 2. 夜間若干電能靠E層反射達較長距離 3. 天波、地波並存 4. 日間及夏季衰減較夜間及冬季為大 5. 使用垂直天線
1. 中波廣播
| 2. 航空及航海通 3. 無線電定 4. 固定行動業 5. 海洋浮標 6. 業餘通信 高頻 | (HF) 3-30 MHz
| 100~10公尺
|
1. 電波利用電離層(特別是F層)反射
(一次或多次反射)以達遠距離
| 2. 傳播情況隨季節及每日時間變化頗大 3. 利用天線指向性,可收小功率達長距離之通信效果 4. 通達距離隨頻率及發射角之不同而異 5. 太陽黑子數越多,電離層密度越大,位置較高,最高可用頻率 (MUF)亦加高,通信距離越長,反之相反 6. 地波距發射機不遠即消失 7. 使用水平天線
1. 長距離點與點通信及廣播
| 2. 業餘通信 3. 無線電天文 4. 標準頻時信號 5. 航空行動 6. 短波廣播 7. 民用無線電 特高頻 | (VHF) 30-300 MHz
| 10~1公尺
|
1. 穿越電離層,較不受其影響
| 2. 以空間波作視距 (line-of-sight)通信 3. 20-65MHz間利用E層散射達視距外通信 4. 使用垂直及水平天線 (水平天線較多) 5. 接近直線傳輸
中距離通信、雷達、調頻廣播、電視、導航、業餘
、無線電叫人、各種陸地行動通信
| 超高頻 | (UHF) 3003,000 MHz
| 100~10公分
|
1. 視距通信
| 2. 以空間波接近直線傳輸 3. 1000MHz以上微波: (1) 使用定向反射面、反射網、喇叭型、 拋物面反射式及平面天線等 (2) 恆向地面彎曲進行 (3) 使用線上保護、熱待接保護及分集式保護等鏈路保護方式 (4) 方向性極高,波束極狹 (5) 發射功率小 (6) 如光波性質,遇阻礙即被吸取 (7) 10GHz以上頻率愈高,受雨點、霧.雪、 雹及空氣中氣體之吸收愈大 (8) 利用對流層散射可達遠距離
短距離通信、中繼系統、
電視、衛星氣象、天文、業餘無線電定位、
助航太空研究、地球探測、公眾行動電話、
有線電話無線主副機、計程車無線電話
| 極高頻 | (SHF) 至高頻 (EHF) 3-300 GHz
| 10~0.1公分
| 同上
|
微波中繼、各種雷達、
衛星通信、衛星廣播、
無線電天文
| |
|---|
| Spectrum Allocation |
|---|
|
RF band for mobile Communication system < 3.5 GHz
|
|
Wireless spectrum is regulated by governments
|
|
Regulation has significant impact on technology
advancement and business development
|
|
Who should use the spectrum? How should it be used?
|
|
Beauty Contest
|
|
Auction for licenses (e.g. 3G license)
|
|
Regulator
|
|
NCC (Taiwan)
|
|
FCC (USA)
|
|
Unlicenced Band (ISM)
|
|
ISM Band (for Industrial, Scientific, and Medical Use)
|
| ITU-R defined ISM Bands |
|---|
| Frequency range [Hz] | Center frequency [Hz] | Availability
| 6.765–6.795 MHz
| 6.780 MHz
| Subject to local
acceptance
| 13.553–13.567 MHz
| 13.560 MHz
| 26.957–27.283 MHz
| 27.120 MHz
| 40.66–40.70 MHz
| 40.68 MHz
| 433.05–434.79 MHz
| 433.92 MHz
| Region 1 only
| 902–928 MHz
| 915 MHz
| Region 2 only
| 2.400–2.500 GHz
| 2.450 GHz
| 5.725–5.875 GHz
| 5.800 GHz
| 24–24.25 GHz
| 24.125 GHz
| 61–61.5 GHz
| 61.25 GHz
| Subject to local acceptance
| 122–123 GHz
| 122.5 GHz
| Subject to local acceptance
| 244–246 GHz
| 245 GHz
| Subject to local acceptance
| |
|---|
|
WLAN
|
| Bluetooth | 2450 MHz band
| HIPERLAN
| 5800 MHz band
| IEEE 802.11
| 2450 MHz and 5800 MHz bands
| |
|---|
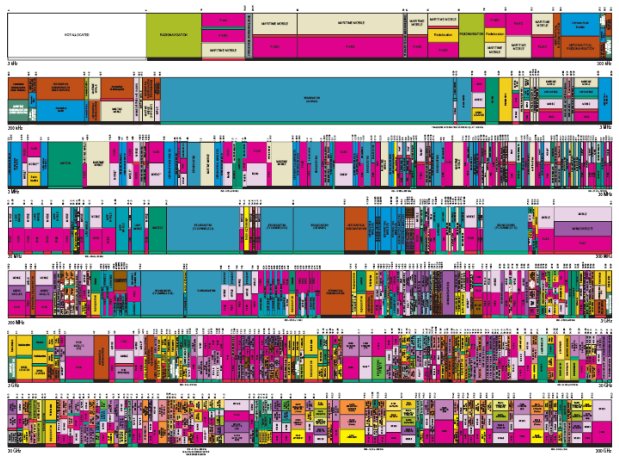
| Spectrum Allocation - US |
|---|
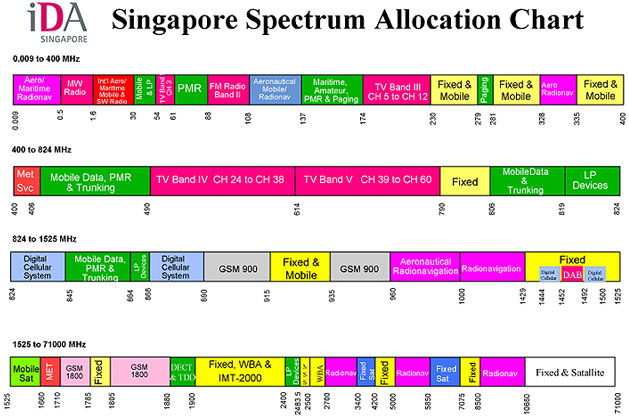
| Spectrum Allocation - Singapo |
|---|
| 最大頻寬限制 |
|---|
|
Nyquist理論 (沒有雜訊)
|
|
D bps = 2 B log 2 K
|
|
Shannon-Hartley Theorem (考慮雜訊)
|
|
C = B log 2 (1 + S/N)
|
| C | the channel capacity in bps
| B
| the bandwidth of the channel, in Hertz
| S
| the total signal power over the bandwidth
| N
| the total noise power over the bandwidth
| S/N
| the signal-to-noise ratio(SNR)
| |
|---|
| Multipath Interference Problem |
|---|

| Fluctuations of SNR |
|---|

|
Path-Loss
|
|
Shadow (Slow) fading
|
|
Fast fading
|
|
Doppler fading
|
| Multipath Interference Problem |
|---|

| 其他干擾 |
|---|
|
ACI (Adjacent Channel Interference)
|
|
兩個相鄰頻率的使用者,可能因距離不同而基地台收取兩者信號時,
因信號強度大幅起落而導致收訊能力大幅降低
|
|
Co-Channel Interference
|
|
兩個相同頻率但不在同cell的使用者,因對基地台的距離不同,導致
弱信號被強信號蓋台
|
| Rain Attenuation |
|---|
|
雨衰 (降雨衰耗)
|
|
降雨衰耗為無線電波在穿過雨區時所受到的衰減量。
|
|
當無線電信號到達天線前,行進的途徑如有烏雲或雨水的阻擋而形成信號衰減,
此種衰減稱為雨衰。
|
| Doppler Effect |
|---|
|
Named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler.
|
|
Change in the observed frequency (or wavelength) of waves due to
relative
motion between the wave source and the observer.
|
|
The Doppler effect is
responsible for the perceived change in pitch of a siren as it
approaches and then recedes, and for the red shift of light
from distant galaxies.
|
| FSK |
|---|

| MultiAccess Technology |
|---|

|
讓多各使用者共用有限的頻譜,以提高系統容量,避免降低系統效能
|
| FDMA |
|---|

每一頻道在任一時刻只能有一個用戶。
如果一個FDMA頻道沒被使用,不能為其他 existing 用戶使用
,這是一種資源浪費。
| FDMA頻道的頻寬為 30kHz。
| 系統複雜度比TDMA低,所須的額外控制資訊比較少。
| 為了減小相鄰頻道干擾,FDMA系統對射頻(RF)濾波器要求較高。
| |
|---|
| TDMA |
|---|


| TDMA Time Frame |
|---|
|
Each channel has 200k Hz
|
|
Each channel is divided by 8 time slots
|
| Preamble 探測序列 |
Information Message
|
Trail Bits |
|---|
| Spread Spectrum |
|---|
|
使用全頻段發射信號
|
|
FHMA (frequency hopped multiple access)
|
|
Invented by George Antheil (a composer)
Hedy Lamarr (an actress, 1913–2000) |
|
Antheil and Lamarr submitted the idea of a
secret communication system in June 1941. On
August 11, 1942, U.S. Patent 2,292,387 was
granted to Antheil and "Hedy Kiesler Markey",
Lamarr's married name at the time. This early
version of frequency hopping used a piano
roll to change between 88 frequencies and was
intended to make radio-guided torpedoes
harder for enemies to detect or jam.
|
|
DSMA (direct sequence multiple access):又稱為CDMA (code
division multiple
access)
|
| CDMA |
|---|

保密性極高
| Qualcomm將CDMA技術商業化
| CDMA具備若干優異的特點
| UMTS或是cdma2000都以CDMA為核心技術
| 使用者共用相同頻率,可以採用TDD或FDD。
| 系統容量限制是軟性的,當使用者數目增加時,雜訊水平(noise
| floor)會上升,系統效 能會因而下降。
| 由於訊號展頻後佔用了相當大的頻段,使得多路徑漸弱效應大減。
| |
|---|
| 雙工 (Full-Duplex) |
|---|
|
以 Full-Duplex 方式讓雙方可同時發話
|
| FDD | 同時提供兩各單工的頻道,須兩組 Transceiver
| TDD
| 同樣的頻率下提供兩個單工的時槽
| |
|---|
| 特性分析 |
|---|
| Pedestrian | Remote/mobile user
| Mobility
| Low
| high
| User density
| high
| hig h/low
| Quality , availablity requirements
| high
| can compromise
| Cost
| moderate
| can compromise
| Handset size
| small
| can be large
| Battery life
| long
| can be short
| Alternative
| wired access
| n.a.
| |
|---|
| Mobile System |
|---|
|
Mobile System Demands BOTH Wireless and Mobility
|
|
A wireless system may not be a mobile system
|