Trend of Telecom Network 電信網路發展趨勢
Trend of Telecom Network 電信網路趨勢
Optical Networks 新興光纖傳輸技術
Optical Ring and ADM
Optical Network
Optical Network
Backbone Example
Backbone Example
Flat Network 扁平化網路
Broadband Access 寬頻接取網路
Voice Over IP
All-IP Networks
All-IP Networks Motivation
All-IP Networks Benefits
New Services 新型跨網路服務
Comparison of network Capability 網路能力比較
All IP Network
All IP Network
All IP Network
SIP, Soft Switches
Packet Voice Network Architecture
3GPP
IETF Standards
Beyond 3G
VoIP Quality Issues
How to reduce network delay?
Classification of Services 應用服務之分類
QoS Demands 應用服務之品質要求
Qos Issues
Open Programming Interface
All-IP vs. PSTN
New Complications
Feature Interactions
Evolution of Telecom 電信網路演進
Conventional Service Model 傳統電信網路之服務模型
IN Service Model 智慧型網路之服務模型
Conclusion
| Trend of Telecom Network 電信網路趨勢 |
|---|
| Optical Networks 新興光纖傳輸技術 |
|---|
|
DWDM (Dense Wave Division Multiplexing)
|
|
在現有的管路基礎上,可大幅提高光纖之頻寬
Increasing bandwidth on current pipelines |
|
頻寬之成本大幅下降
bandwidth cost decreasing |
|
傳輸距離 (Transmission Distance)
|
|
新的光纖技術可傳數百公里而不需再放大 (can transmit several hundread km without repeaters)
|
|
傳統銅線只能傳送數公里 (copper wire can only transmit several km)
|
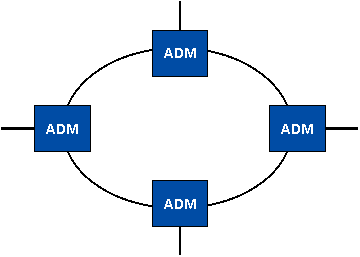
| Optical Ring and ADM |
|---|
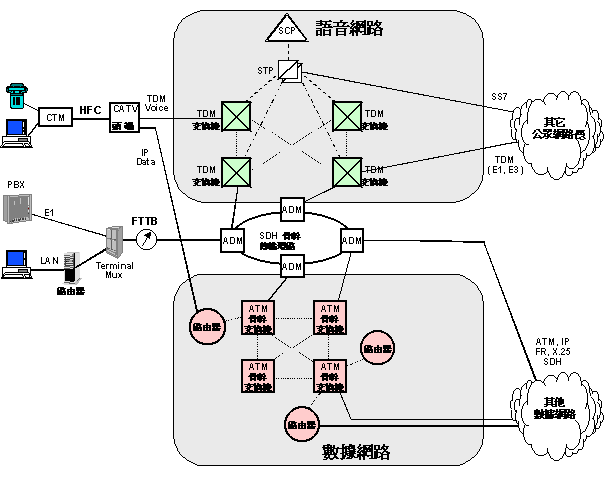
| Optical Network |
|---|
| Optical Network |
|---|
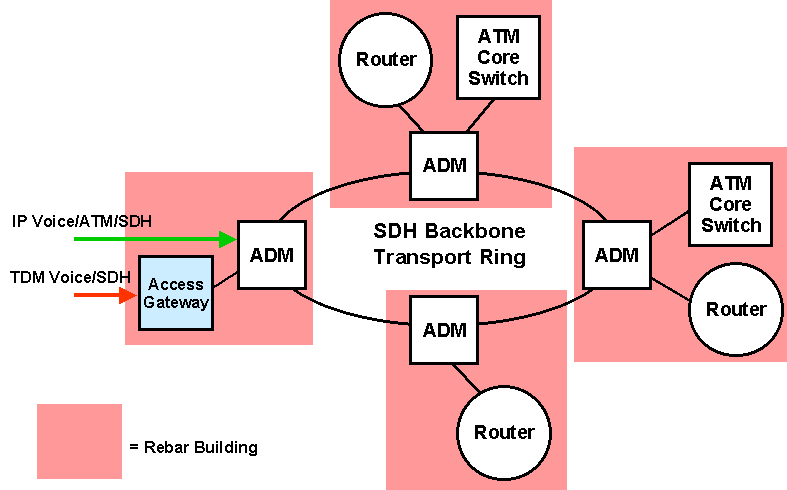
| Backbone Example |
|---|
| Backbone Example |
|---|
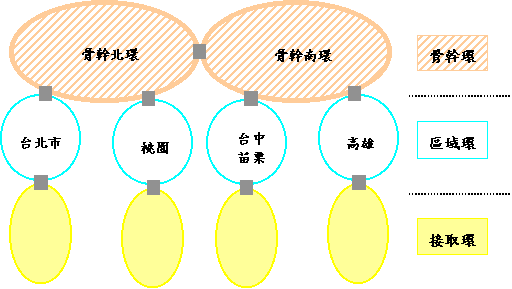
|
North Ring
|
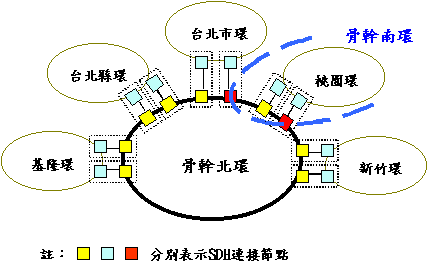
|
South Ring
|
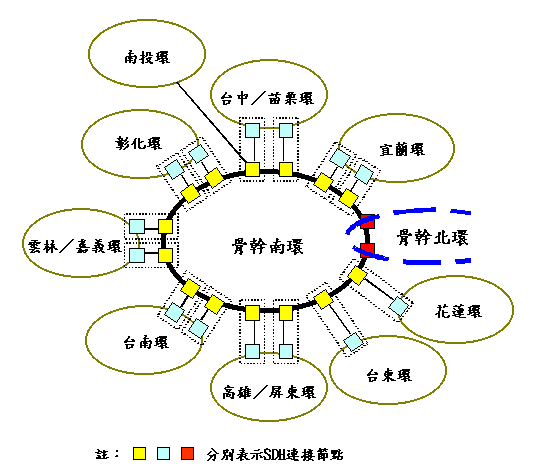
| Flat Network 扁平化網路 |
|---|
| Network Class | 接取網路 (Access) | 交換機配置 (Switch) | 管理
(Management)
| 傳統網路 (Conventional)
| 銅絞線 (Copper)
| 小而多 (small and many)
| 管理麻煩而費用高昂 (difficult and expensive)
| 新興網路 (Emergent)
| 光纖 (optical)
| 大而少 (large and few)
| 管理簡單費用較低 (Easy and low cost)
| |
|---|
|
傳統電信網路 (Conventional Telecom Networks)
|
|
受制於電話與交換機間之距離限制,每個交換機所能涵蓋
範圍較小,必須使用許多交換機,管理麻煩而費用高昂
limited by the distance betweeen phone sets and siwtches, each switch can only cover a small area so that a network needs many switches to form the network. Therefore, the manegement is difficult and expensive. |
|
新興電信網路 (Emergent Telecom Networks)
|
|
電話與交換機間之距離可達數百公里,每個交換機所能涵蓋
範圍可以很大,可以使用較少之大型交換機,管理費用較低,
The distance betweeen phone sets and siwtches can be as long as several hundread km, each switch can cover a large area so that a network needs fewer switches to form the network. Therefore, the manegement is easier and cheaper. |
|
有利於話務量較少之新興業者 (good for new and small operators)
|
|
必須佈建 Access Nodes 到各地區, 將話務集中於光纖, 再轉送交換機進行交換 Need to use access nodes to concentrate customers and transfer traffic to switches |
|
Access Node 扮演角色,類似行動電話網路之基地台
An access node acts like a Base Station in a cellular network |
|
顛覆傳統 (Against Common Wisdom)
|
|
在花蓮市內互打電話,需連到台北,在台北相連(交換)
Two phones next to eacher other may be switched in a remote location |
|
市內電話走的距離比長途電話長
a local call may travel longer than a long-distant call |
| Broadband Access 寬頻接取網路 |
|---|
|
寬頻接取網路是新興固網公司之成敗關鍵 (baordband access is the key to success)
|
|
市內電話之建設是獲取執照之條件 (local network is mandatary for operation licence)
|
|
傳統市內電話已無成長空間,必須搶佔寬頻接取市場 (Local phone market is alreay saturated, muct more to broadband access)
|
|
可用技術 (Available Technologies)
|
| FTTB | FTTC | ADSL | HFC | LMDS |
|---|
|
市場策略 (Market Strategy)
|
|
以FTTB/FTTC搶佔都會區商業客戶 (Use FTTB/FTTC to attract business customers)
|
| Voice Over IP |
|---|
| VoIP over public Internet | Quality unacceptable
| VoIP over Private Internet (ISP)
| Controlled quality, limited functionality, Niche market
| VoIP over Private Network (Telecom Operator)
| Full Functionality, Dominant market
| |
|---|
|
第二類電信 ISP 經營網路電話之利基 (Niche of ISP on VoIP)
|
|
有效運用頻寬 (Efficient use of Bandwidth)
|
|
使用語音壓縮技術,減少頻寬需求 (Use compression to reduce bandwidth reuirement)
|
|
可針對實際需求租用頻寬 (On-demand bandwidth lease)
|
|
Bypass 普及服務義務 (BY pass USO)
|
|
第二類電信 ISP 經營網路電話之隱憂 (Problems of ISP on VoIP)
|
|
必須與第一類電信業者共同,承擔普及服務義務, 國際電話不再有鉅額利潤 Need to share USO and other public duty |
|
只能提供基本電話服務,無法提供智慧型網路的服務機能
Basic services only, no advanced services such as IN |
|
第一類電信業者正試圖運用 VoIP 技術,第二類業者將失去利基
|
| All-IP Networks |
|---|
| All-IP Networks Motivation |
|---|
| All-IP Networks Benefits |
|---|
| New Services 新型跨網路服務 |
|---|
| Comparison of network Capability 網路能力比較 |
|---|
| All IP Network |
|---|
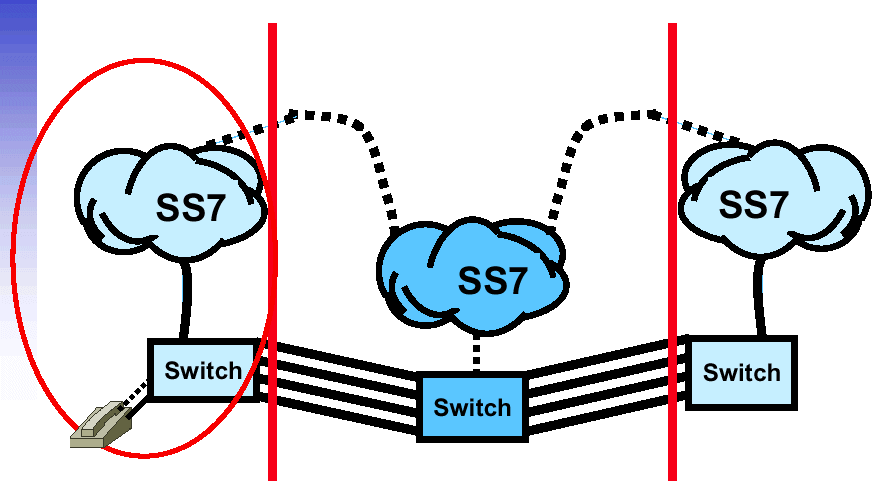
| All IP Network |
|---|
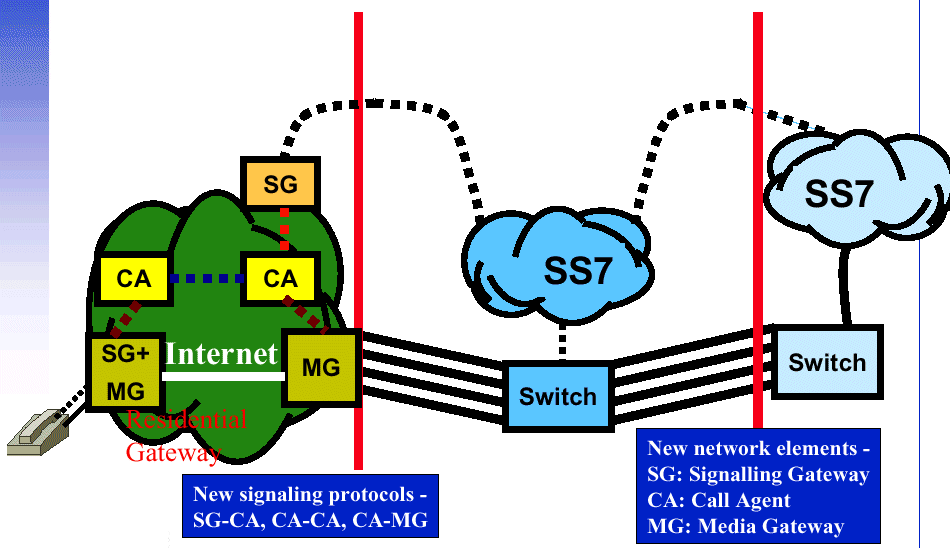
| All IP Network |
|---|
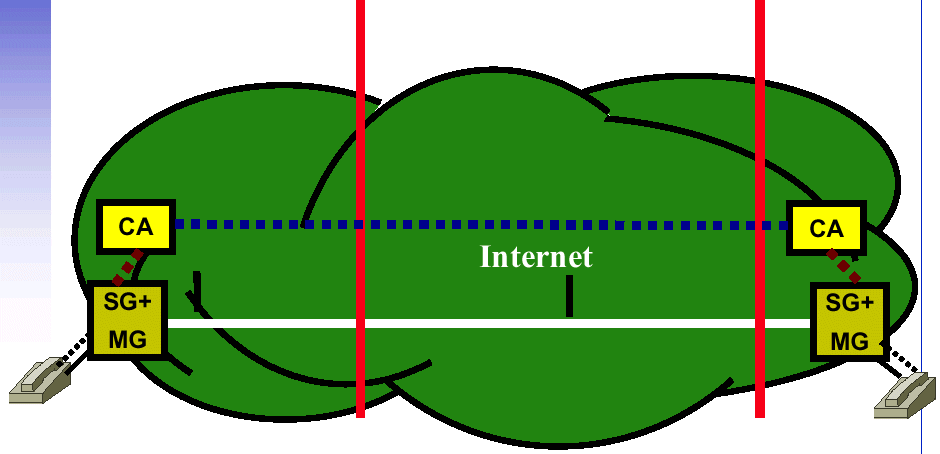
| SIP, Soft Switches |
|---|
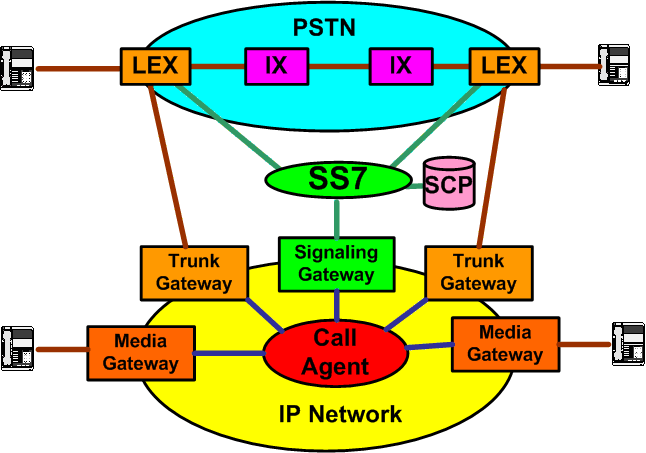
| Packet Voice Network Architecture |
|---|
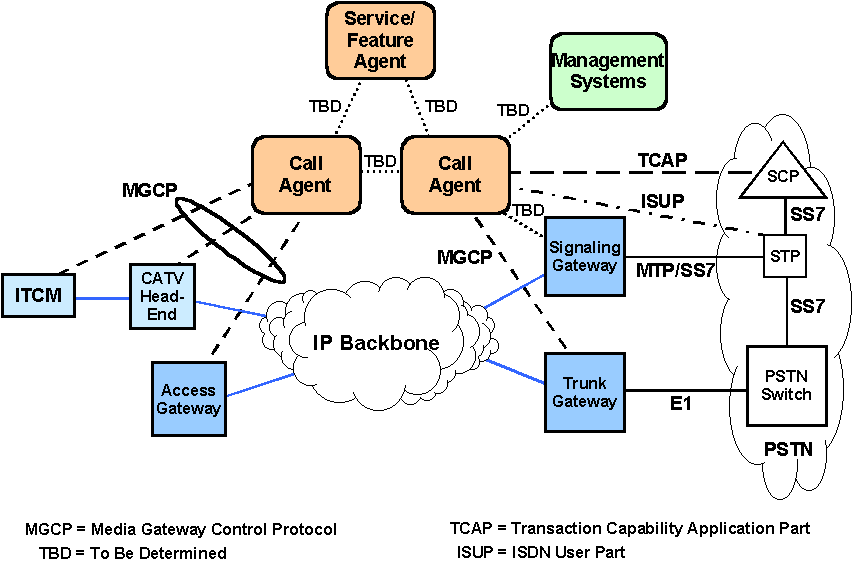
| 3GPP |
|---|
|
(Packet SW + Circuit SW ) * ( Fixed + Mobile )
|
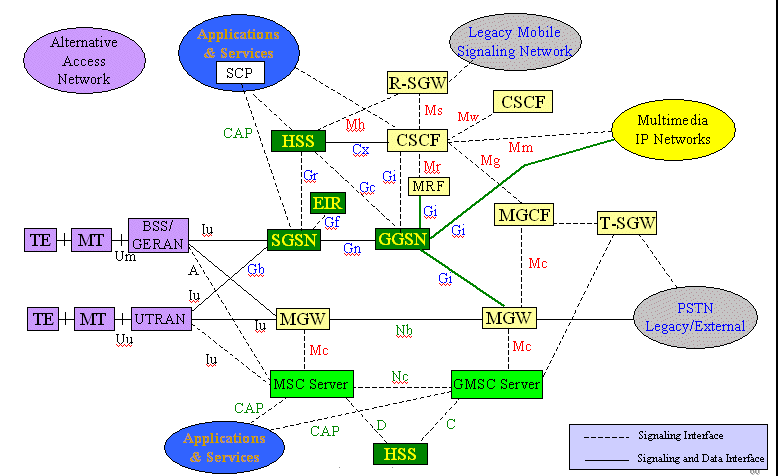
| IETF Standards |
|---|
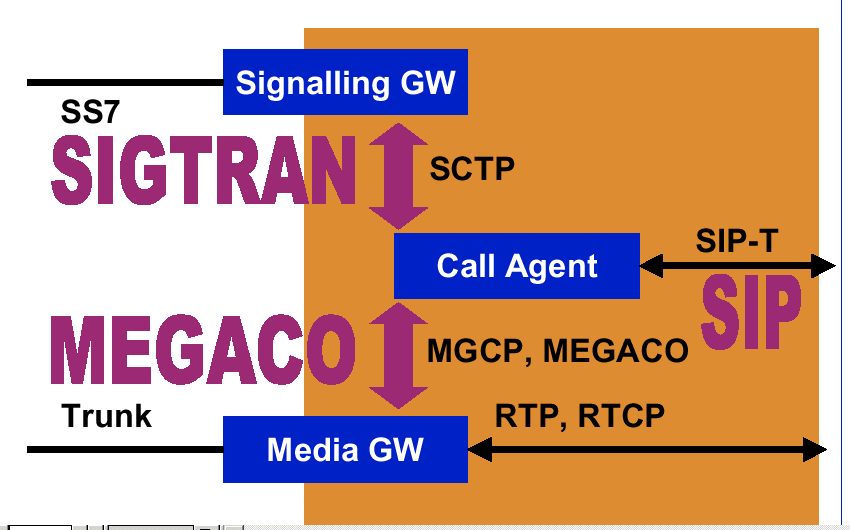
| Beyond 3G |
|---|
| VoIP Quality Issues |
|---|
|
Quality parameters
|
| Delay | Packet Loss | Jitter |
|---|
|
Cause of Delay
|
| accumulation delay | processing delay | network delay |
|---|
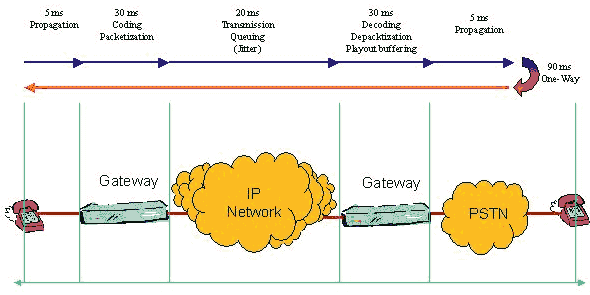
|
Reducing delay time is a key problem to VoIP
|
| How to reduce network delay? |
|---|
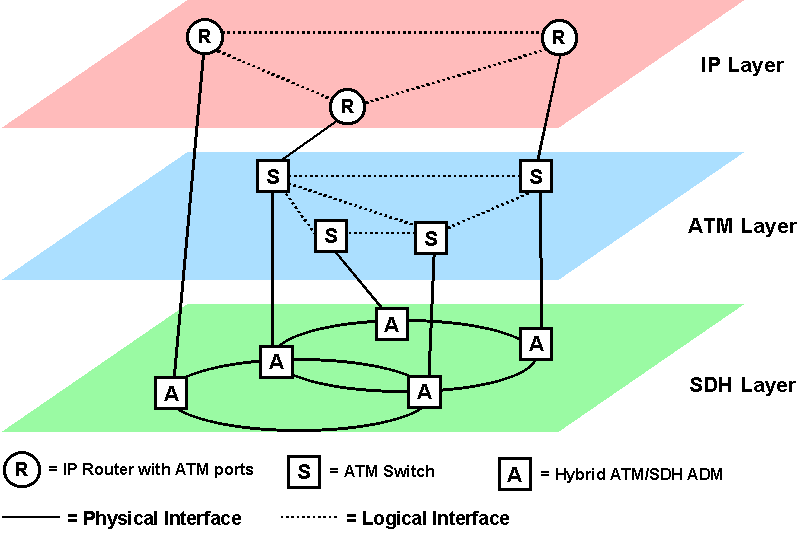
|
IP over ATM
|
|
Level 2 Switch, MPLS
|
|
IP over SDH
|
|
IP over Fiber
|
| Classification of Services 應用服務之分類 |
|---|
| QoS Demands 應用服務之品質要求 |
|---|
| Qos Issues |
|---|
| Open Programming Interface |
|---|
| All-IP vs. PSTN |
|---|
| New Complications |
|---|
| Feature Interactions |
|---|
| Evolution of Telecom 電信網路演進 |
|---|
|
Based on service complexity viewpoint
|
| 時代(Era) | 提供服務 (Services) | 代表技術 (Technology) | Local Market | Long Distance Market | 網路互連 (Inerconnection)
| 傳統網路 | Conventional basic calls
| 5ESS
| 獨佔 | Monopoly 獨佔 | Monopoly 單純 Simple
| | 智慧型網路 | IN simple features
| AIN
| 獨佔 | Monopoly 開放 Deregulated
| 稍複雜 | 未來網路 | (B3G) complicated features
| A lot
| 開放 | Deregulated 開放 | Deregulated 非常複雜 | Very Complicated |
|---|
| Conventional Service Model 傳統電信網路之服務模型 |
|---|
|
Service Logic Distribution of Conventional Networks
|
|
Fixed routing
|
|
Fully Duplicated service logic
|
|
Only good for Basic calls and simple service features (CW, CF)
|
|
Difficult to add and to change service features
|
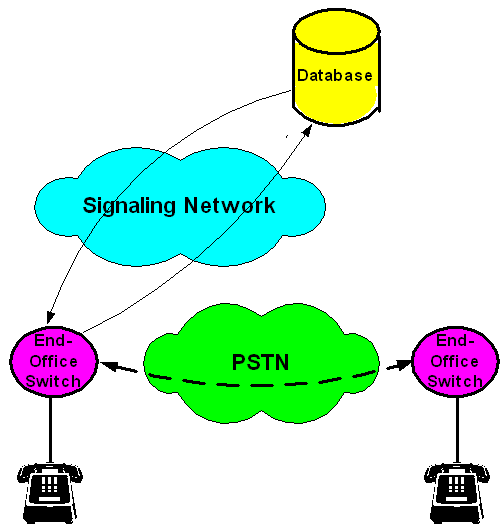
| IN Service Model 智慧型網路之服務模型 |
|---|
|
智慧型網路 (Intelligent Network) Service Logic Distribution
|
|
Centralized Control
|
|
Easy to add and change simple features (800/080)
|
|
Limited communications between switches and SCPs
|
|
Not good for complicated features
|
| Conclusion |
|---|
⊕ 電信網路是國家基礎建設 (Network is a Key of National Infrastructure)
⊕ 電信網路龐大、複雜 (Network is Compilcate)
|
異質性太高,各層同時快速演進 (Network is heterogeneous and Evolve
|
⊕ 網路革命之追求目標 (Objective of Network Revolution
| 單純化 (Simplification) | 彈性化 (Flexibility) | 經濟有效 (Cost Effective) |
|---|