Routing
Introduction
Distance Vector Concept
Distance Vector: Update
Distance Vector: Network Discovery
Distance Vector: Topology Change
Link State Concept
Link State: Update
Link State: Network Discovery
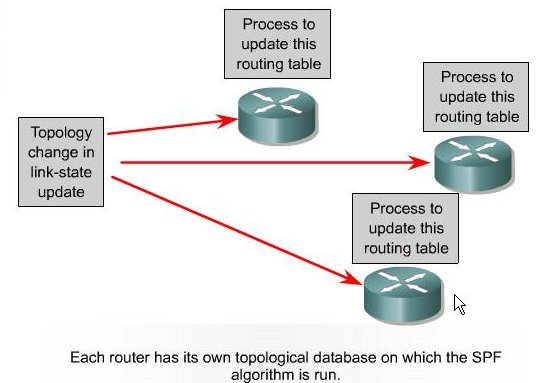
Link State: Topology Change
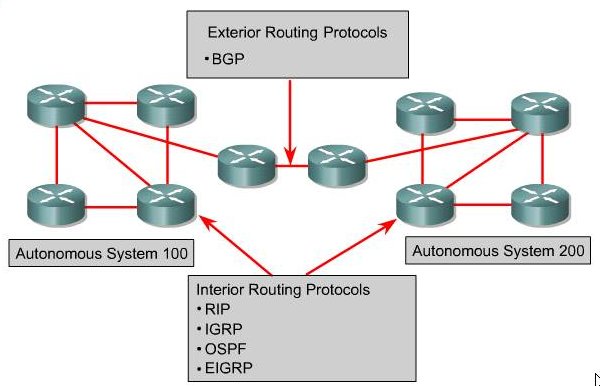
Interial and Exterior Routing
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP)
Summary
Comparison
Link State vs Distance Vector
Reference
| Introduction |
|---|
⊕ Static Routing
⊕ Dynamic Routing
♦ Distance Vector
RIP、IGRP、BGP
♦ Link State
OSPF、IS-IS
| Distance Vector Concept |
|---|
| Distance Vector: Update |
|---|
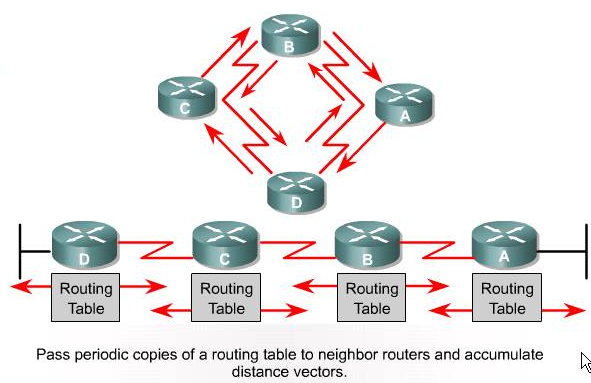
| Distance Vector: Network Discovery |
|---|
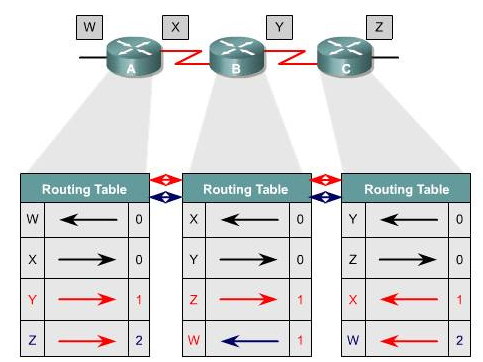
| Distance Vector: Topology Change |
|---|

| Link State Concept |
|---|
| Link State: Update |
|---|
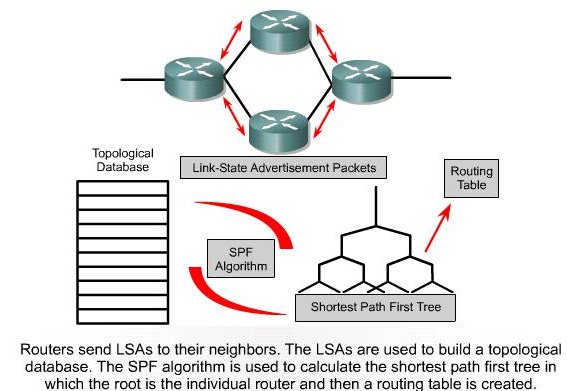
| Link State: Network Discovery |
|---|
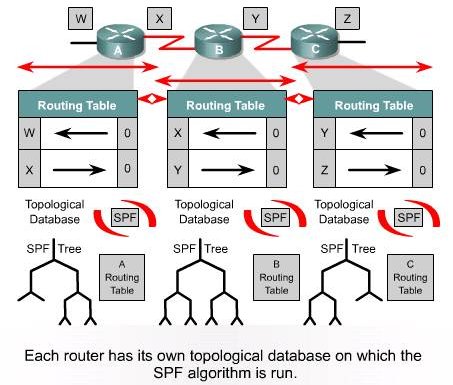
| Link State: Topology Change |
|---|
| Interial and Exterior Routing |
|---|
| Routing Information Protocol (RIP) |
|---|
♦ Distance vector routing protocol
♦ Path weight: hop count
♦ If the hop count is greater than 15, the packet is discarded
♦ Routing updates are broadcast every 30 seconds, by default IGRP
Sun Feb 6 13:07:14 CST 2011| Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) |
|---|
♦ Distance vector routing protocol.
♦ Path Weight: Bandwidth, load, delay and reliability
♦ Routing updates are broadcast every 90 seconds, by default
Sun Feb 6 13:07:14 CST 2011| Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) |
|---|
♦ Link-state routing protocol
♦ Uses the SPF algorithm to calculate the lowest cost to a destination.
♦ Routing updates are flooded as topology changes occur
Sun Feb 6 13:07:15 CST 2011| Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) |
|---|
♦ Distance vector exterior routing protocol.
♦ Used between ISPs or ISPs and clients.
♦ Used to route Internet traffic between autonomous systems
Sun Feb 6 13:07:15 CST 2011| Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) |
|---|
♦ Uses load balancing
♦ Uses a combination of distance vector and link-state features.
♦ Uses Diffused Update Algorithm (DUAL) to calculate the shortest path.
♦ Routing updates are broadcast every 90 seconds or as triggered by topology changes.
Sun Feb 6 13:07:15 CST 2011| Summary |
|---|
| Protocol | Description | Charateristics
| Distance Vector
| RIPv1 and RIPv2
| Interior Gatway Routing Protocol(IGRP)
|
Link-State
| Open Shortest Path First(OSPF)
| Intermediate-System to Intermediate-System(IS-IS) |
|
|---|
| Comparison |
|---|
| Distance Vector | Link State
| View network from neighbor's perspective
| Get common view of entire network topology
| Add distance vectors form router to router
| Caculate the shortest path to other routers
| Frequent periodic updates: | slow convergence Event triggered upfates: | faster convergence Passes copies of routing tables to neighbor routers
| Passes Link-State routing updates to other routers
| |
|---|
| Link State vs Distance Vector |
|---|
| Advantages | Disadvantages
| Fast convergence: changes are reported
immediately by the source affected
| Significant demands on memory and processing resources
| Robustness against routing loops
| Requires very strict network design
| Routers know the topology
| Requires a knowledgeable network administrator
| Link-state packets are sequenced and aged
| Initial flooding can impede network performance
| The link-state database sizes can be
minimized with careful network design
| |
|---|
| Reference |
|---|