Disk
Secondary Storage
Magnetic Disk Storage
Improving Disk Drive Performance
Personal Computer Storage
Optical Storage
Data Organization
File Organization
Processing Data into Information
| Secondary Storage |
|---|
⊕ Benefit
♦ Economy
♦ Reliability
♦ Convenient
⊕ Magnetic Tape
♦ Forms (inch in Width)
1/2 inch-wide tape wound on reel
1/4 inch-wde tape in cartridges andcassettes
♦ Amount of Data measure by density
character per inch (cpi)
byte per inch (bpi)
♦ Data Representation
tracks or channels (9 tracks)
one crose section represents one EBCDIC (8+P) character
♦ Magnetic Tape Unit (Tape Drive)
read/write head
erase head
supply reel and take-up tape
♦ Blocking
Interblock gap (IBG) or Interrecord gap (IRG)
♦ Digital Audio Tape (DAT) and Helical Scan Recording
Sat Feb 5 07:27:05 CST 2011| Magnetic Disk Storage |
|---|
⊕ Hard Disk
Faster, expensive, large capacity
♦ Traditional
♦ Winchester
sealed module, chaper, more convenient.
used by all PC's
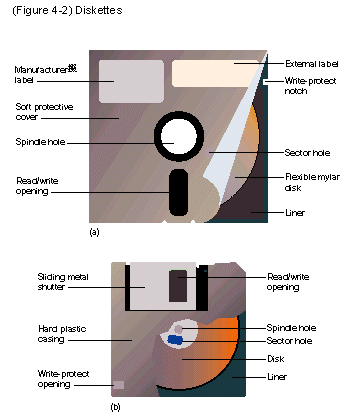
⊕ Diskette (Floppy Disk)
Slower, cheap, small capacity
⊕ Data Organization On Disks
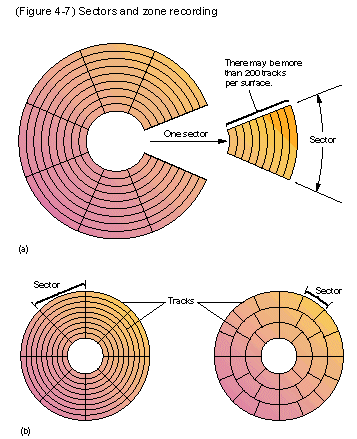
♦ Sector Method
Data are referred by surface #, track #, and sector number
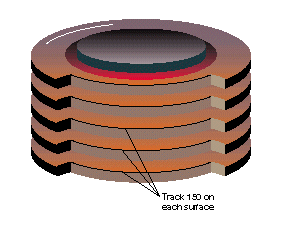
♦ Cylinder Method
all the vertical tracks ofone cylinder are accessible by the read/write heads wit one positioning of the access arms mechanism.
⊕ Disk Access to Data
♦ Seek time
♦ Head Switching
♦ Rotation Delay
♦ Data Transfer
♦ Average access time 9ms to 40ms (could be slower)
Sat Feb 5 07:27:05 CST 2011| Improving Disk Drive Performance |
|---|
⊕ Caching
♦ use cache to stored used data in main memory for later reuse
♦ Hit rate (Hit ratio)
♦ Data Synchronization (data sync)
write-through
write-back
⊕ Zone Recording
⊕ Data Compression
⊕ Using several disk together
♦ Disk Mirroring
♦ RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks)
Sat Feb 5 07:27:05 CST 2011| Personal Computer Storage |
|---|
⊕ Diskettes (Floppy Disks)
3.5"/1.44M, 5.25"/1.2M
⊕ Hard Disks
5.25", 3.5" Wenchester (Full Height, Half Height, Quater Height)
540Mbyte, 1 Gbyte, cost several thousand dollors NT.
For Notebook PCs, 1.8", 1.3" (Kitty Hawk, 20Mbyte)
⊕ Removable Storage
⊕ Hard Cards
⊕ RAM disks
⊕ Flash Memory
 |  |  |  |
|---|
⊕ Flash Memory (行動碟)
 |  |
|---|
⊕ Backup System
Sat Feb 5 07:27:06 CST 2011| Optical Storage |
|---|
⊕ How it work?
♦ Write Operation
Use powerful laser beam to hit up a spot on the surface
♦ Read Operation
Use a laser beam to light up the spot to read back the data by detecting the difference in reflection
Mostly Read-only
♦ Write-once, read-many (WORM)
♦ CD-ROM (Compact Disk read-only memory)
Sat Feb 5 07:27:06 CST 2011| Data Organization |
|---|
⊕ Character
♦ a letter, number, or special character
⊕ Field
♦ a set of related characters
⊕ Record
♦ a collection of related fields
⊕ File
♦ a collection of related records
⊕ Database
♦ a collection of interrelated files stored together with minimum redundancy
Sat Feb 5 07:27:06 CST 2011| File Organization |
|---|
⊕ Sequential File Organization
♦ records are organized in sequential order by key.
⊕ Direct File Organization
♦ records are organized randomly
♦ Use Hashing techniques
⊕ Indexed File Organization
♦ Combination of both
♦ indexes are sequentially ordered
♦ data record are randomly stored
⊕ Why is tape still needed?
Sat Feb 5 07:27:06 CST 2011| Processing Data into Information |
|---|