Softswitch
Overview
Overview
改變 Telecom 生態
Telephone Network
IN Components
Softswitch Architecture
Softswitch Architecture
Softswitch Architecture
Open Architecture
SoftSwitch Software Architecture
Example: LNP
Example: CID
Softswitch Protocols - MEGACO
Softswitch Protocols - IETF SIGTRAN
SS7 Signaling Points
SS7 Protocol Stack
SS7 Protocol Stack
SIGTRAN Protocol Stack
SIGTRAN Protocol Stack
ISUP-SIGTRAN Conversion
SCCP-SIGTRAN Conversion
TCAP-SIGTRAN Conversion
Softswitch Protocols - SIP
SIP Servers
SIP-T (SIP for Telephone)
SIP-T References
SIP-TSI
Open API: JAIN
Open API: JAIN
Applying JAIN to Softswitch
Servise API: Parlay
Basic Call Control
IN Call Control
Inter-Softswitch Communications
Softswitch Networks
Softswitch-SIP Networks
| Overview |
|---|
|
Emulating Circuit Switch in Software
|

| Overview |
|---|
|
Provides Open Layered Architecture
|

| Circuit-Switched | Soft-Switched
| solutions in a proprietary box
| Solutions are open standards-based
| Expensive
| Customers choose best-in-class products
| LIttle room for innovation
| Open standards enable lower cost for innovation
| |
|---|
| 改變 Telecom 生態 |
|---|
|
Integration/Incorporation
|
|
Convergence of voice and data
|
|
Combination of telecom and Internet Technologies
|
|
Reuse PSTN database and INservices in packet networks
|
|
Multiple sources for ap development and deployment
|
|
Standardization
|
|
standard interface (protocols) for communications
|
|
Open standard (APIs) for service creation
|
|
Customized services created by users themselves
|
|
Better scalability
|
| Telephone Network |
|---|

| IN Components |
|---|

| SSP | Service Switching Point | switching, signaling, routing, service invocation
| STP
| Service Transfer Point
| signaling, routing
| SCP
| Service Control Point
| service logic execution
| SDP
| Service Data Point
| subscriber data storage, access
| IP
| Intelligent Peripheral
| resource such as customized voice announcement, voice recognition, DTMF digit collection
| |
|---|
| Softswitch Architecture |
|---|

| Softswitch Architecture |
|---|

| Softswitch Architecture |
|---|
|
Media Gateway Controller (MGC)
|
|
provide basic call control, signaling, etc.
|
|
manages resources, generate CDR
|
|
Application Service (AS)
|
|
hosts enhanced services:
|
|
calling card, 800/080 translation, voice mail, follow-me
|
|
porvides service/AP interfaces
|
|
access to underlying service and switching functions
|
|
Media Controller (MS)
|
|
Provdes specialized resources:
|
|
IVR, conferencing, facsimile functions
|
|
AS can access MSto utilize resurces on MS
|
| Open Architecture |
|---|

| SoftSwitch Software Architecture |
|---|

| Example: LNP |
|---|
|
LNP (Local Number Portability)
|

| Example: CID |
|---|
|
CID (Call ID Delivery)
|

| Softswitch Protocols - MEGACO |
|---|

| Softswitch Protocols - IETF SIGTRAN |
|---|
| SS7 Signaling Points |
|---|

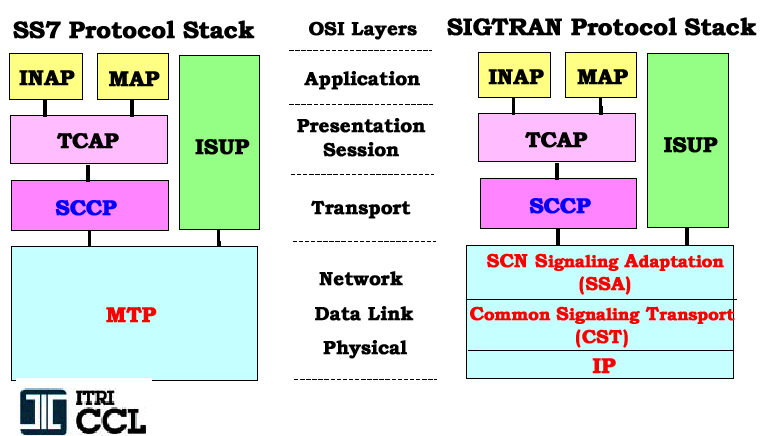
| SS7 Protocol Stack |
|---|

| SS7 Protocol Stack |
|---|
| INAP | IN Application Part | | MAP
| Mobile Application Part
| | TCAP
| Transaction Capabilities Application Part
| |
SCCP
| Signaling Connection Control Part
|
|
MTP
| Message Transfer Part | Level 3 |
MTP
| MTP | Level 2
Providing error detection/correction and sequenced delivery of the SS7 messages
| MTP
| MTP | Level 1
Defining the physical, electrical,and functional characteristics of the digital signaling link
| |
|---|
| SIGTRAN Protocol Stack |
|---|

| SIGTRAN Protocol Stack |
|---|

| ISUP-SIGTRAN Conversion |
|---|

| SCCP-SIGTRAN Conversion |
|---|

| TCAP-SIGTRAN Conversion |
|---|

| Softswitch Protocols - SIP |
|---|
|
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) ITIF RFC 2543
|
| User Agents | Client and Server
| Servers
| Registrar, Proxy, Redirect Server
| |
|---|

| SIP Servers |
|---|

| SIP-T (SIP for Telephone) |
|---|

| SIP-T References |
|---|
| Encapsulation of ISUP in the SIP body | draft-ietf-sip-isup-mime-08
| Translation of ISUP Info. in the SIP header
| draft-ietf-sip-isup-header-00
| Use of INFO Method for mid-call signaling
| draft-ietf-sip-isup-method-05
| |
|---|
| SIP-TSI |
|---|
|
SIP-TSI (SIP for Telephony Service Interface )
|
|
Proposed in the International Softswitch Consortium (ISC)
|
|
Not an IETF standard or an Internet Draft
|

| Open API: JAIN |
|---|
|
JAIN (Java APIs for Integrated Networks)
|
|
Goals
|
|
Network Convergence - Any network
|
|
Secure network access - By anyone
|
|
Service/Ap portability - Write once, run anywhere
|
|
Protocol API Specifications
|
|
Interfaces to PSTN, IP, ATM, wireless
|
|
Abstract the details of networks and protocol
|
|
Application API Specifications
|
|
Interface required for service creation
|
|
Allow for the development of portable applications
|
| Open API: JAIN |
|---|

| Applying JAIN to Softswitch |
|---|

| Servise API: Parlay |
|---|
|
Goal: Network independent and application portability
|

| Basic Call Control |
|---|

| IN Call Control |
|---|

| Inter-Softswitch Communications |
|---|

| Softswitch Networks |
|---|

| Softswitch-SIP Networks |
|---|
