Skype
References
What is Skype?
Skype Network
Super Nodes
Initial 7 Super Nodes
Port
Key Components of the Skype
Skype Functions
Startup
Login
Login Algorithm
Login Process
Login
User Search
Establishment and Teardown
Media Transfer and Codec
Conference
Security
Recommendations
| References |
|---|
| An Alalysis of the Skype Peer-to-Peer Internet Telephony, | Salman A. Baset and Henning Schulzrinne, | Department of Computer Science Columbia University,New York NY 10027
| Voip and Skype Security,
| Simson L. Garfinkel,
| MIT Computer Science and Atificial Intelligence Laboratory
| |
|---|
| What is Skype? |
|---|
|
A peer-to-peer VOIP client developed by KaZaa
|
|
Users can place voice calls and send text messages to other users of Skype clients
|
|
|
|
特色:
|
|
音質超優,傳遞不延遲
|
|
不怕防火牆阻擋
|
|
語音資料加密,不怕被竊聽
|
|
可同時支援5個人線上聊天
|
|
1.2版後改善聯絡人隨帳號帶著走功能,重裝電腦聯絡人不消失
|
|
語音信箱功能
|
|
Video
|
| Skype Network |
|---|
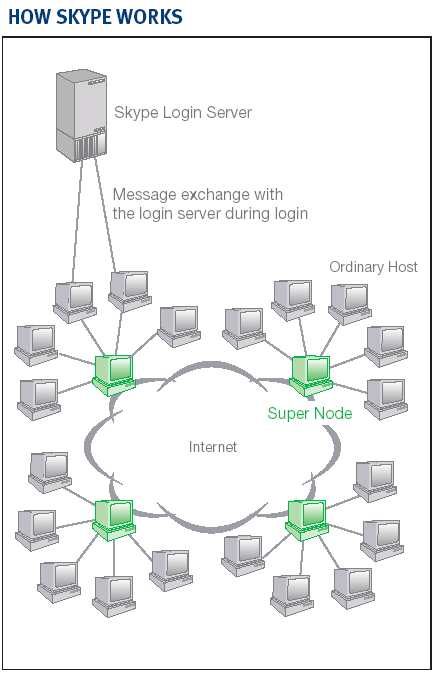
|
Supernode
|
|
Any node with a public IP address having sufficient CPU, memory, and
network bandwidth is a candidate to become a super node
|
|
Ordinary host
|
|
A ordinary host must connect to a super node and must register itself
with the Skype login server for a successful login
|
|
Login Server
|
|
The only central component in the Skype network.
|
|
User names and passwords are stored at the login server
|
| Super Nodes |
|---|

| Initial 7 Super Nodes |
|---|


| Port |
|---|

| Key Components of the Skype |
|---|
|
Buddy List
|
|
Skype stored buddy list in the login server and copy a list in the
windows folder which is a Skype personal profile
|
|
C:\\Documents and Settings\users\Application data\Skype\account\config.xml
|
|
Encryption
|
|
uses 256-bit encryption
|
|
uses 1536 to 2048 bit RSA to negotiate symmetric AES keys
|
|
NAT and Firewall
|
|
SC uses a variation of the STUN and TURN protocols to determine the type of
NAT and firewall it is behind
|
| Skype Functions |
|---|
|
Startup
|
|
Login
|
|
User Search
|
|
Media Transfer and Codecs
|
| Startup |
|---|
|
After installation,
SC run for first time,
it sent a HTTP 1.1 GET request to the Skype server (skype.com).
The first line of this request contains the keyword ‘installed’
|
|
During subsequent startups,
a SC only sent a HTTP 1.1 GET request to the Skype server (skype.com)
to determine if a new version is available.
It contains the keyword 'getlatestversion’
|
| Login |
|---|
|
SC authenticates its user name and password with the login server
|
|
Advertises its presence to other peers and its buddies
|
|
Determines the type of NAT and firewall it is behind
|
|
Discovers online Skype nodes with public IP address
|
| Login Algorithm |
|---|
 |
 |
| Login Process |
|---|
|
After installation and first time startup, HC was observed empty
|
|
Bootstrap Super Nodes
|
|
After login for the first time after installation, HC was initialized
with seven IP:port called Bootstrap Super Nodes
|
|
User Search
|
 |
 |
 |
| Login |
|---|
|
First-time Login
|
|
SC sends UDP packets to some bootstrap SNs
|
|
SC establishes a TCP connection with the bootstrap SNs that respond
|
|
SC perhaps acquires the address of login server from SNs
|
|
SC establishes a TCP connection with login server exchange authenication information
|
|
Subsequent Login
|
|
SC uses login algorithm to determine at least one available peer and establishs a TCP connection
|
|
HC was periodically update with new peers
|
| User Search |
|---|
|
Skype uses Global Index technology to search for a user
|
|
Skype claims that search is distributed and is guaranteed to find a user if it exists and has logged in during last 72 hours
|
|
Search results are observed to be cached at intermediate nodes (3~4 seconds)
|
| Establishment and Teardown |
|---|
|
Call signaling is always carried over TCP
|
|
For user not present in buddy list,
call placement is equal to user search plus call signaling
|
|
If both caller and callee were on public IP address,
caller SC established a TCP connection with the callee SC
|
|
If caller is behind port-restricted NAT and callee is on public IP,
signaling and media flow through an online Skype node
(acts as media proxy)
which forwards signaling to callee over TCP and routes media over UDP
|
|
If both users are behind port-restricted NAT and UDP-restricted firewall,
both caller and callee SC exchange signaling over TCP with another online
Skype node (acts as media proxy),
which also forwards media between caller and callee
|
|
During call tear-down,
signaling information is exchanged over TCP between caller and callee
|
| Media Transfer and Codec |
|---|
|
If both Skype clients are on public IP address,
then media traffic flowed directly between them over UDP. (3~16 kbytes/s)
|
|
If either caller or callee or both were behind port-restricted NAT,
they sent voice traffic to another online Skype node(media proxy) over UDP.
(5 kbytes/s)
|
|
If both users were behind port-restricted NAT and UDP-restricted firewall,
then caller and callee sent and received voice over TCP from another online
Skype node(media proxy). (5 kbytes/s)
|
|
Skype allows peers to hold a call.
To ensure UDP binding,
a SC sends three UDP packets per second to the call peer on average
|
|
No silence suppression is supported in Skype (靜音壓縮)
|
|
The min. and max. audible frequencies Skype codecs allow to pass through are
50 Hz and 8000 Hz
|
|
Uplink and downlink bandwidth of 2 KB/s each is necessary for reasonable
call quality
|
|
Keep-alive Messages - SC sent a refresh messages to its SN over
TCP every 60 second
|
| Conference |
|---|
|
A acts as a mixer, mixing its own packets with those of B and sending to C
|
|
For a three party conference, Skype does not do full mesh conferencing
|
|
The most powerful machine will be elected as conference host and mixer
|
|
Two-way call:36 kb/s, Three-way call:54 kb/s
|

| Security |
|---|
| Privacy | Outside-to-eavesdrop on a conversation?
| Authenticity
| Are you sure that you are reaching the user whose username you specify?
| Availability
| Can Skype always work if both participants are on the internet?
| Survivability
| Can skype users continue to communicate while the network is damaged?
| Resilience
| Can Skype users quickly reestablish communication with each other?
| Integrity (Conversation)
| Dose Skype loose bits of a conversation in progress?
| Integrity (System)
| How does the use of Skype affect other applications running on the
user/s computer and network?
| |
|---|
| Recommendations |
|---|
|
Make sure that any computer used for Skype is free of all spyware,
adware, remote-control programs, worms, and computer viruses.
|
|
Username/passward useage,changed issues
|
|
There should always have alternative techniques for contacting each other if
Skype system could become permanently unavailable
|
|
Always independently verify the identiy of a person that you are
communicating with if sensitive material is going to be exchanged
|
|
A buffer-overflow in the voice decoder would enable another Skype user
to execute commands on any system that the user was in contact with
|
|
Skype is apparently encrypted,no way to assure that the person you are
communicating with is not,themselves,recording the conversation in which
you are engaging
|