DCCP
Is Data Rate a Big Issue?
Data Rate Control
UDP and TCP
Transport Protocol
What makes a good Congestion Control?
TCP Congestion Control
AIMD Additive Increase/Multiplicative Decrease
Bandwidth Competition Capability
Problem
DCCP
TFRC (TCP-Friendly Rate Control)
Experimental Fairness Study
Formula of Throughput Calculation for CCID 3
Throughput Competition: UDP vs. NewReno
Throughput Competition: DCCP vs. NewReno and Vegas
Summary of Fairness Study
Quality of VoIP - Coexisting with NewReno
Quality of VoIP - coexisting with Vegas
Quality of VoIP
Where is the Problem?
Motivation of Flexible Bit Rate
Experiment of Flexible Bit Rate
Detection of Network Congestion
Proposed Congestion Control
Performance Evaluation
Speex Codec
Performance of UDP based VoIP
Performance of DCCP based VoIP
Summary of Performance Evaluation
Conclusion
| Is Data Rate a Big Issue? |
|---|
Data Rate
Is Data Rate a Big Issue? |
|---|
| Data Rate Control |
|---|
|
What is proper data rate?
|
|
How to determine proper data rate?
|
|
Which component control data rate?
|

| UDP and TCP |
|---|
|
Every network application is trying to acquire sufficient bandwidth from network
|
|
It also has to prevent the network from congestion Congestion Control
|
|
Congestion Control Adpotion Approaches
|
| No control | e.g. choose an initital data rate, then use UDP to send data
| Use TCP
| Easy and nice to network, but not adequate for real time applications
| Embedded in Application
| e.g. Skype
| |
|---|
| Transport Protocol |
|---|
|
A transport protocol enables two hosts to establish a connection and
exchange streams of data.
|
|
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
|
|
doesn't guarantee data delivery
|
|
constant packet rate, no congestion control
|
|
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
|
|
guarantee data delivery
|
|
with congestion control
|
|
require possitive acknowlegement
|
|
Tahoe, Reno, New Reno, SACK, Vegas
|
| What makes a good Congestion Control? |
|---|
|
Short packet transmission time
|
|
Maximize throughput
|
|
Minimize retransmission
|
|
Maintain network harmony and fairness
|
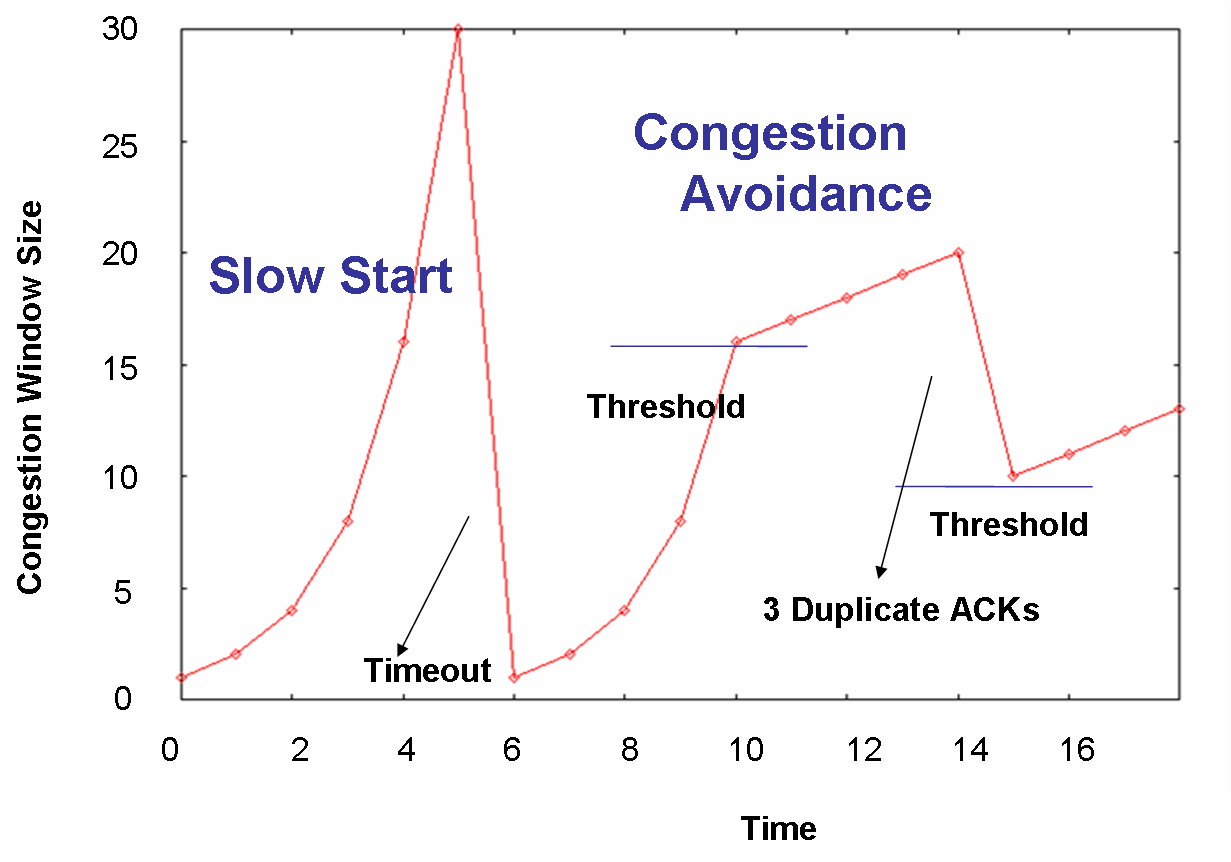
| TCP Congestion Control |
|---|
|
use Sliding Window to control data transmission
|

|
data transmission is clocked by ACK
|
|
CWND (Congestion Window Slize) Control
|
|
Event Driven by packet loss --- trial-and-error
|
|
Calculation by RTT (Run Trip Time)
|
|
Calculation by packet loss rate
|
| AIMD Additive Increase/Multiplicative Decrease |
|---|
| Bandwidth Competition Capability |
|---|

| Problem |
|---|
|
UDP doesn't care network congestion at all
|
|
TCP compromises itself on network congestion
|
|
congetion control mechanism takes effect
|
|
provide buffering effect for network traffic
|
|
So far so good, but
|
|
Not tolerable in the future - too many multidedia applicaitons
|
|
Degradatin of Buffering effect
|
| DCCP |
|---|
|
DCCP (Datagram Congestion Control Protocol)
|
|
UDP + Congestion Control
|
|
is proposed to replace UDP to support real time application with congestion control
|
|
CCID 2 - TCP-like Congestion Control (AIMD Sliding window)
|
|
CCID 3 - TFRC Congestion Control
|
|
Question: Work or not?
|
|
Elements of Evalution
|
|
Bandwidth competition
|
|
Quality support for real-time applications (VoIP)
|
| TFRC (TCP-Friendly Rate Control) |
|---|
|
Designed for streaming applications
|
|
Receiver measures loss event rate and returns it to the sender.
|
|
Sender uses this feedback messages to calculate RTT
|
|
Sender uses RTT and loss event rate to calculate data rate
|

| s | Packet Size
|
R
| Round Trip Time
|
p
| Loss Event Rate
|
t_RTO
| TCP Retransmission Timeout Value
|
b
| # of Packets Acknowledged by a Single TCP ACK
| |
|---|
| Experimental Fairness Study |
|---|
 |
|
| Formula of Throughput Calculation for CCID 3 |
|---|

| Throughput Competition: UDP vs. NewReno |
|---|
| UDP first | NewReno First
|
| 
|  |
|---|
| Throughput Competition: DCCP vs. NewReno and Vegas |
|---|
| DCCP first | NewReno First
|
| 
|  DCCP first
| Vegas First
|
| 
|  |
|---|
| Summary of Fairness Study |
|---|
 |
| ||||
|
| |||||
| DCCP run first, one out of five TCPs was injected every 10 seconds |
|---|
| Quality of VoIP - Coexisting with NewReno |
|---|
| |||||||
| Avg. Delay Time | Avg. Loss Rate
|
| 
|  | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of VoIP - coexisting with Vegas |
|---|
| ||||
| Avg. Delay Time | Avg. Loss Rate
|
| 
|  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of VoIP |
|---|
| Throughput Ratio |
|
| 
|
Avg. Delay Time
| Avg. Loss Rate
|
| 
|  |
|---|
| Where is the Problem? |
|---|
|
VoIP prefers constant packet stream
|
|
Change of Inter-packet time will delay packet arrival time
|
|
Better alternative:
|
|
Change packet size, but not inter-packet time
|
|
Flexible VoIP bit rate, Constant inter-packet time
|

| Motivation of Flexible Bit Rate |
|---|
|
Hypothesis: Use lower bit rate in congestion may have higher quality
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
Experiment (real network in lab environment with Speex Codec)
|

| Transmitted packets | Received packets | Bit Rate | Loss Rate | MOS
| 326
| 326
| 7.75
| 0
| 3.01
| 326
| 326
| 9.8
| 0
| 3.30
| 326
| 305
| 12.8
| 0.064
| 3.22
| 326
| 279
| 16.8
| 0.1285
| 2.15
| 326
| 254
| 20.6
| 0.2225
| 1.81
| |
|---|
|
Results
|
|
Use lower bit rate in congestion may have higher quality
|
| Experiment of Flexible Bit Rate |
|---|

| Detection of Network Congestion |
|---|
|
Change of Run Trip Time
 |
|
|
| Proposed Congestion Control |
|---|
|
If Network Congestion Detected
Then, activate congestion control - lower bit rate |
|
If in lower bit rate state, raise bit rate by one level for every
b second
|
when receive a new packet at T i ,Then t new =T i -T i-1 if t new >= t avg +3σ t and congestion frequency >= α send decrease bitrate command to sender congestion frequency=0 else if t new >= t avg +3σ t congestion frequency=congestion frequency+1 else congestion frequency=0 calculate new t avg and new σ t fi |
|---|
| Performance Evaluation |
|---|
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Parameter | Value
| Packet Size
| 15-106 Kbytes (Payload only)
| Inter Packet Interval
| 30 ms
| VoIP Codec
| Speex
| Link Bandwidth
| Up Link : 2 Mbps | Down Link: 10 Mbps # of VoIP session
| 0-100
| |
|---|
| Speex Codec |
|---|
|
|
| Performance of UDP based VoIP |
|---|
 |
 | ||||
| |||||
| Performance of DCCP based VoIP |
|---|
| DCCP with constant bit rate | DCCP with variable bit rate
|
| 
| 
| 
| 
|
| |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summary of Performance Evaluation |
|---|
 |
 |
| Conclusion |
|---|
|
DCCP Based VoIP has poor performance when other TCPs (except Vegas) coexist
|
|
Flexible bit rate VoIP can maintain quality while doing congestion control
|
|
Need to improve DCCP
|
|
Challenge: To maintain the separation between Applicaiton and Transport layers
|
