GPRS
GPRS 簡介
GPRS Logical Architecture
GPRS Architecture
GPRS Network Elements
SGSN and GGSN Functionalities
GPRS Data Transfer
GPRS Addressing
GPRS GPRS Multislot Capabilities
GPRS Core Network
GPRS Protocol Layer
Protocol Stack for Tunneling
GPRS Authentication
MS State Model
MS Attach
MS Dettach
Signal Flow
PDP Activation
PDP Context Activation - 1
PDP Context Activation - 2
PDP Context Activation - 3
PDP Context Activation - 4
Location Management
GPRS Mobility Management
Roaming
Roaming in GPRS
Using Access Point in Home PLMN
Roaming Arrangements between Operators
External Network Connections:
Transparent access to the Internet
Internet Access - Large Subscriber Base
IP Address Translation
Access to Intranets
Access to Intranets: VPN
GPRS Management Functions
GPRS OA&M Architecture
GPRS Core Network Management
MS Class
GPRS Charging
Security Consideration
Using Access Point in Home PLMN
| GPRS 簡介 |
|---|
|
Concept
|
|
packet switching
|

|
Connection Mode
|
| GSM w/o GPRS | end-to-end transmission
| GSM with GPRS
| link-by-link transmission
| |
|---|
|
Flexible Bit Rates
|
|
from < 100 bit/s to over 100 kbit/s.
|
|
Network Elements
|
Serving GPRS Support Nodes SGSN
| Gateway GPRS Support Nodes GGSN
| GPRS backbone
| Point-to-multipoint Service Centre PTM SC
| |
|---|
|
Additional Facilities
|
| GPRS-specific mobility management: the location of the MS is handled separately by the SGSN and by the MSC/VLR even if some cooperation exists network management capable of handling the GPRS-specific elements
| a new air interface for packet traffic
| new security features for the GPRS backbone and a new ciphering algorithm
| new MAP and GPRS-specific signalling
| |
|---|
| GPRS Logical Architecture |
|---|

| GPRS Architecture |
|---|

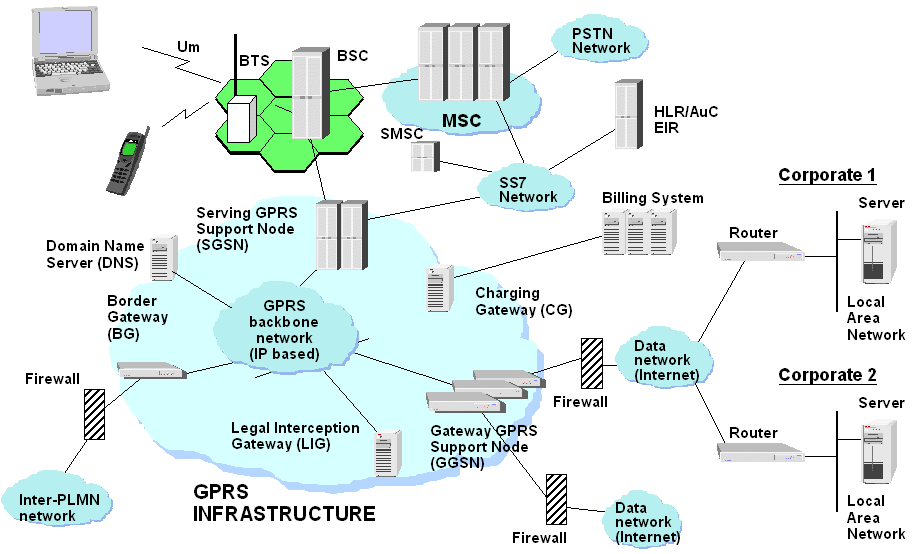
| GPRS Network Elements |
|---|

| SGSN | Serving GPRS Support Node
| GGSN
| Gateway GPRS Support Node
| NMS
| Network Management System
| BG
| Border Gateway
| CG
| Charging Gateway
| FW
| Firewall
| LIG
| Lawful Interception Gateway
| |
|---|
|
Additional Facilities
|
| GPRS-specific mobility management: the location of the MS is handled separately by the SGSN and by the MSC/VLR even if some cooperation exists network management capable of handling the GPRS-specific elements
| a new air interface for packet traffic
| new security features for the GPRS backbone and a new ciphering algorithm
| new MAP and GPRS-specific signalling
| |
|---|
| SGSN and GGSN Functionalities |
|---|
| SGSN | GGSN
| |
|
|
|---|

| GPRS Data Transfer |
|---|

Wed Mar 16 00:26:44 CST 2011
GPRS Addressing

Core Network and the GPRSsubscribers use different IP address spaces
Core invisible to subscribers and vice versa
Core carries subscriber traffic in GPRS Tunnel
GPRS GPRS Multislot Capabilities

GPRS Core Network
SGSN
GGSN
Border Gateway
DNS
NMS
Charging Gateway
Wed Mar 16 00:26:45 CST 2011
GPRS Protocol Layer

Protocol Stack for Tunneling

GPRS Authentication

MS State Model

MS Attach

MS Dettach

Signal Flow

PDP Activation
PDP
Packet Data Protocol (e.g. IP)
MS
Mobile Station
TE
Terminal Equipment
PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol
PDP Context Activation - 1


PDP Context Activation - 2

PDP Context Activation - 3
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service

PDP Context Activation - 4

Location Management
MS sends Routing Area Update Request to SGSN
The SGSN validates the MS's presence in the new RA.
If OK SGSN updates MM context for the MS
Routing Area Accept message returned to MS
MS sends Routing Area Update Request to new SGSN
New SGSN sends context request to old SGSN
Old SGSN sends response and starts tunnelling data to new SGSN
The new SGSN sends "Update PDP Context Request" to GGSN
The new SGSN informs HLR of the SGSN change by sending "Update Location" to HLR
HLR sends "Cancel Location" to old SGSN

GPRS Mobility Management

Roaming

Roaming in GPRS

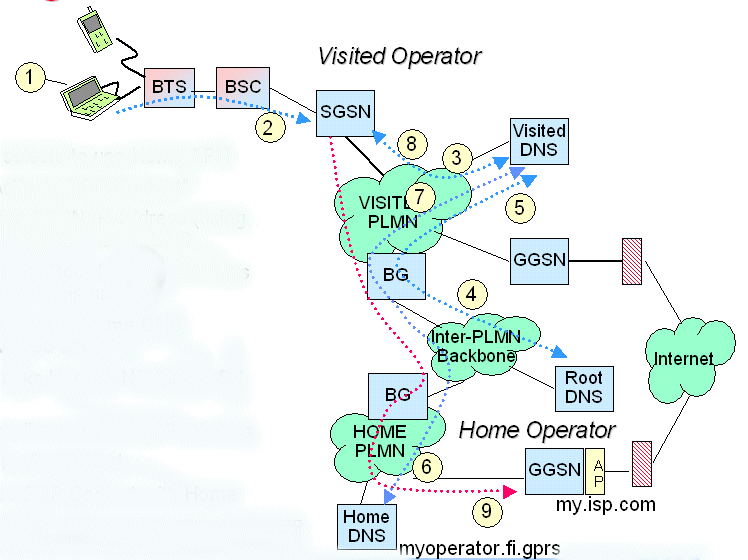
Using Access Point in Home PLMN
1. Visiting user selects to use Home APN
2. MS sends "Activate PDP Context"
3. SGSN asks for GGSN IP address (using APN as the key) from Visited DNS
4. Visited DNS asks Root DNS "who knows the IP address for this name ?"
5. Root DNS replies the Home DNS address to Visited DNS
6. Visited DNS asks Home DNS for GGSN address
7. Home DNS replies the GGSN IP address
8. Visited DNS replies SGSN
9. SGSN creates PDP Context with Home GGSN
Roaming Arrangements between Operators
Wed Mar 16 00:26:56 CST 2011
External Network Connections:
Wed Mar 16 00:26:57 CST 2011
Transparent access to the Internet

Internet Access - Large Subscriber Base

NAT
Network Address Translation
IP Address Translation
10.1.1.1
123.45.40.1:61001
10.1.1.2
123.45.40.1:61002
10.1.1.3
123.45.40.1:61003
10.1.1.4
123.45.40.1:61004
10.1.1.5
123.45.40.1:61005
…
…
10.1.1.254
123.45.40.1:61254
+ Less public IP addresses needed
+ Security: private addresspace invisible to the Internet
- IP Multicast does not work
- IPsec does not work
Access to Intranets

RADIUS
One widely used protocol/method for dynamic IP address allocation and user authentication
Access to Intranets: VPN

GPRS Management Functions
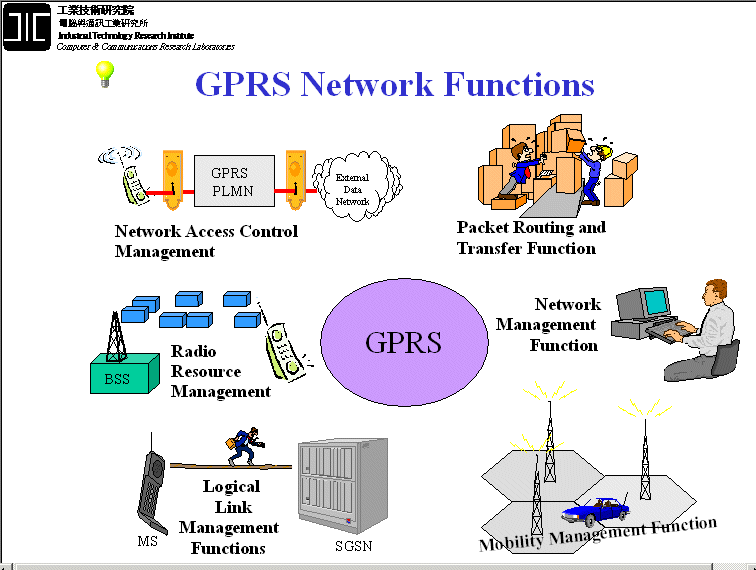
GPRS OA&M Architecture

GPRS Core Network Management
Wed Mar 16 00:27:02 CST 2011
MS Class

GPRS Charging
Mobility management data
Duration of PDP context
Data volume uplink/downlink
Usage of external networks (= Access Point)
SGSN & GGSN address

Wed Mar 16 00:27:03 CST 2011
Security Consideration
GPRS mobile users
External networks
Operator's personnel
Other mobile networks
Malfunctioning equipment
Crash of network
Access to management, charging etc. information
Misconfigure the network
Denial of service. lower QoS
Information confidentiality
Integrity and authenticity
etc.
Physical security against network element access
Host authentication
Ciphered links
Personnel security with authorization
Using Access Point in Home PLMN
